Climates of the Mediterranean During the Neolithic Transition
A Quantitative Approach Using the Köppen Classification and Radiocarbon Dating
University of Oxford
Università di Pisa
University of Cambridge
Introduction
Climate & Chronology series  15 October 2024, University of Oxford
15 October 2024, University of Oxford
An ecological and economic revolution

Late Foragers and Early Farmers
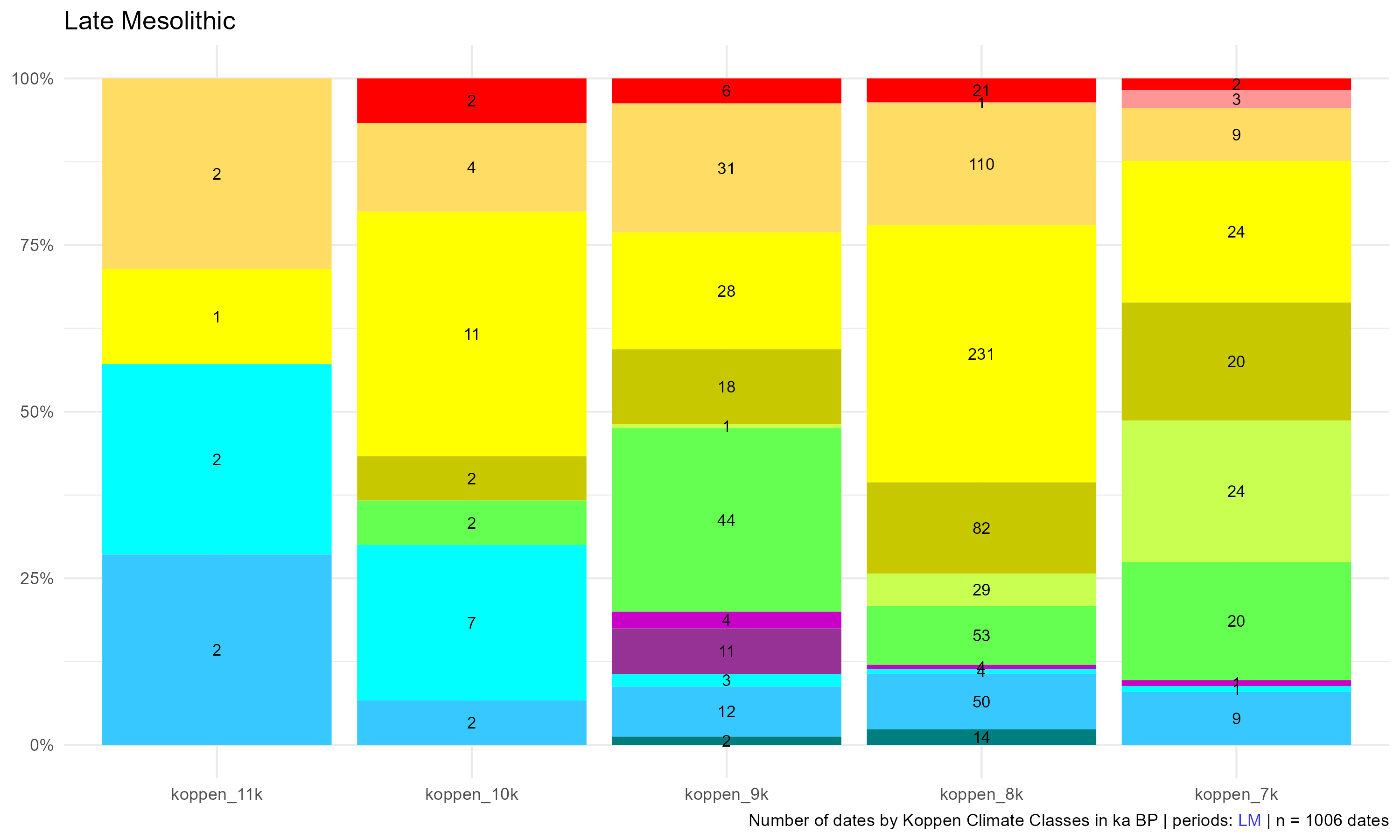
Late Mesolithic (LM), Late Foragers.
 @ChatGPT
@ChatGPT
Residenciality increase
Circular mobility to access discontinuous resources in time and space (seasonality)
Low demography
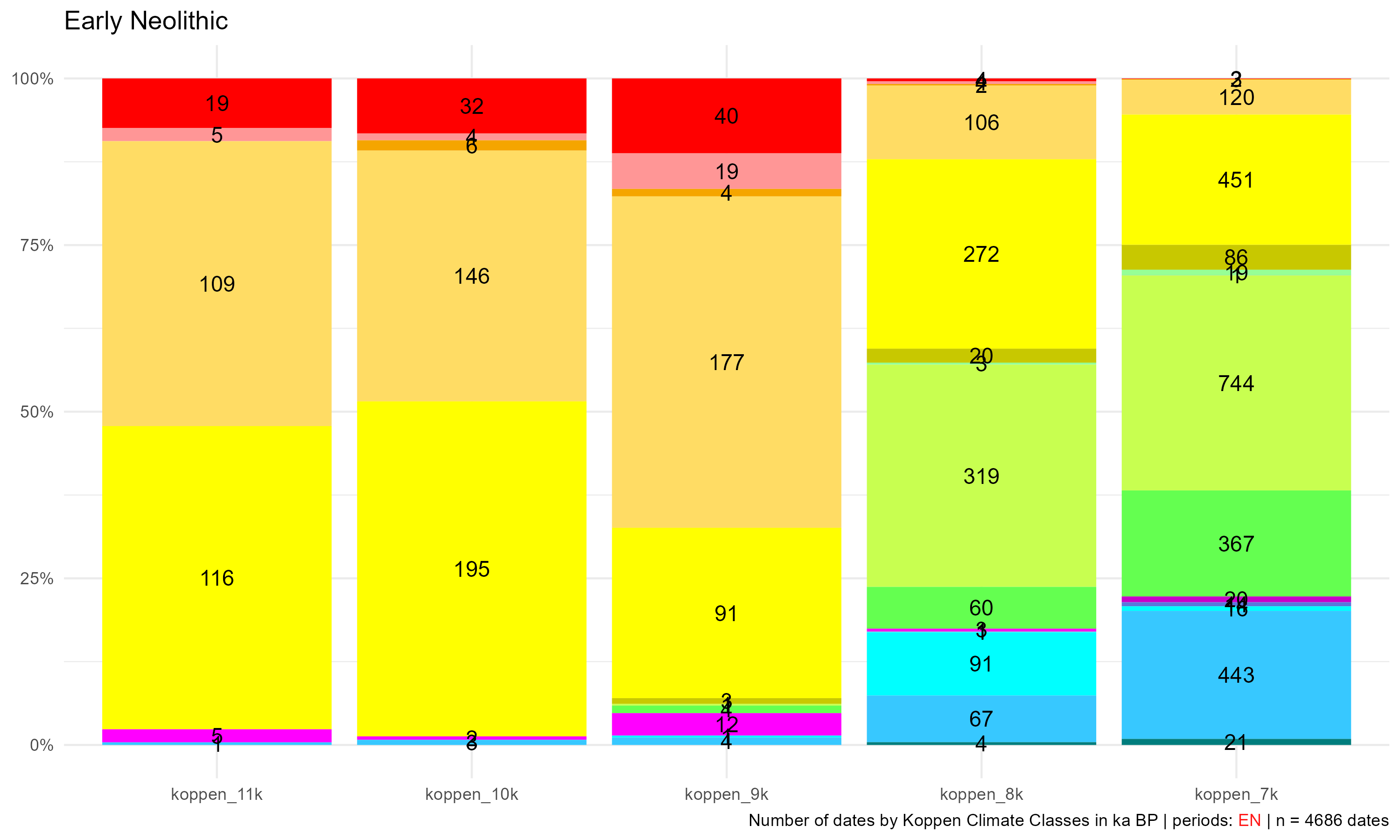
Early Neolithic (EN), Early farmers.
 @ChatGPT
@ChatGPT
Permanent settlements
Logistic mobility to access localized resources for farming economy
High demography
Framework
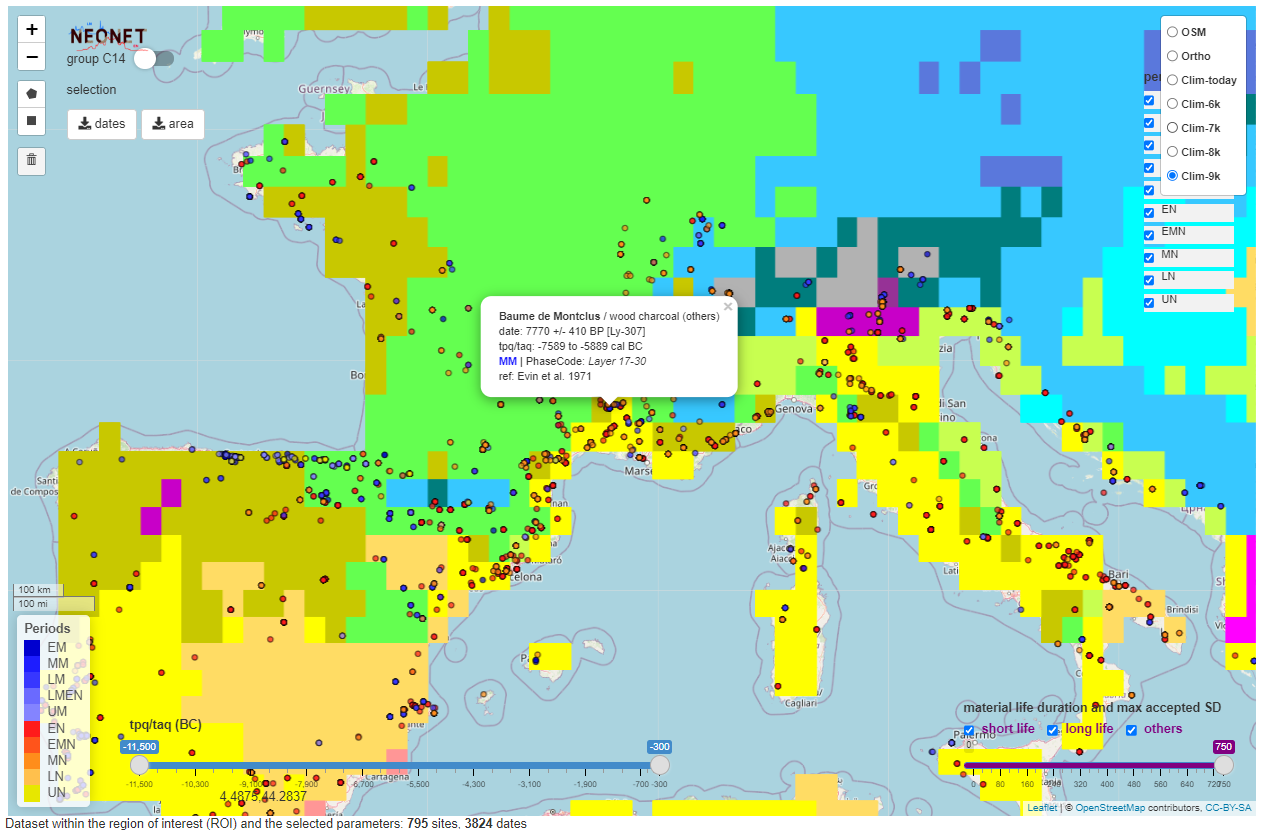
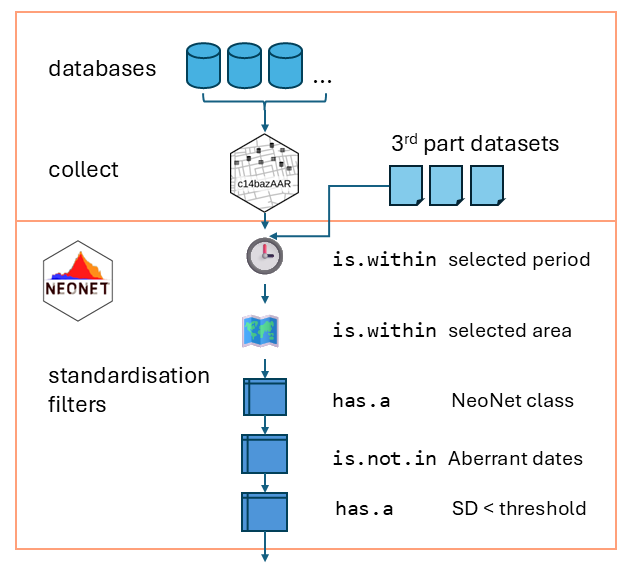
Neonet project
Early Mesolithic (EM)
Middle Mesolithic (MM)
Late Mesolithic (LM)
Early Neolithic (EN)
Middle Neolithic (MN)
Late Neolithic (LN)
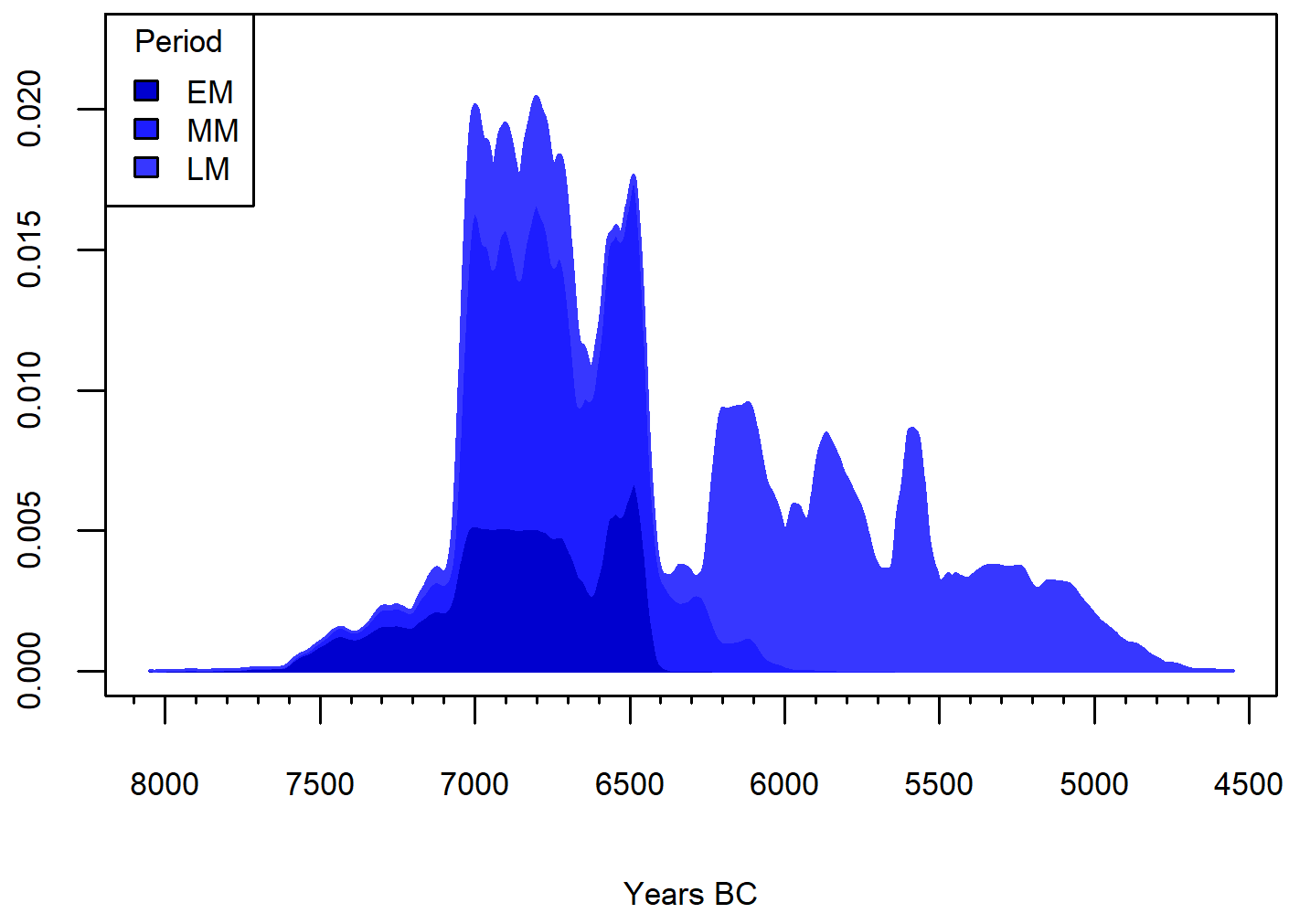
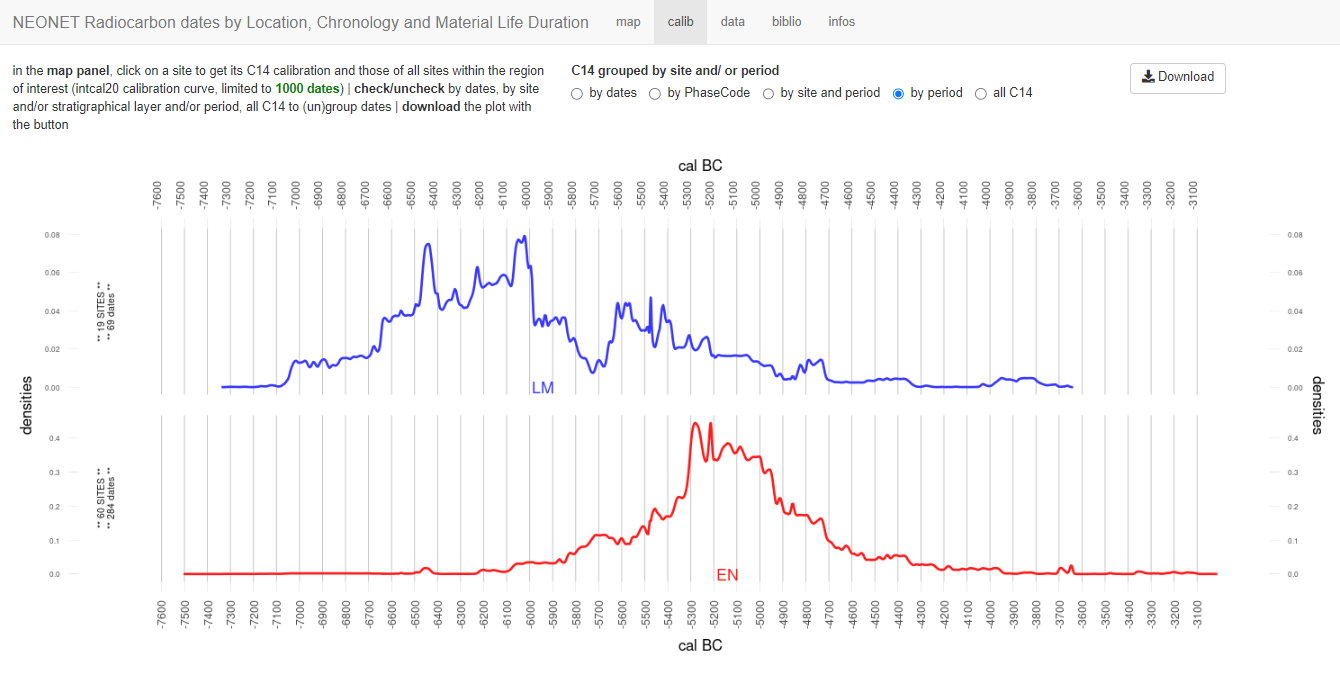
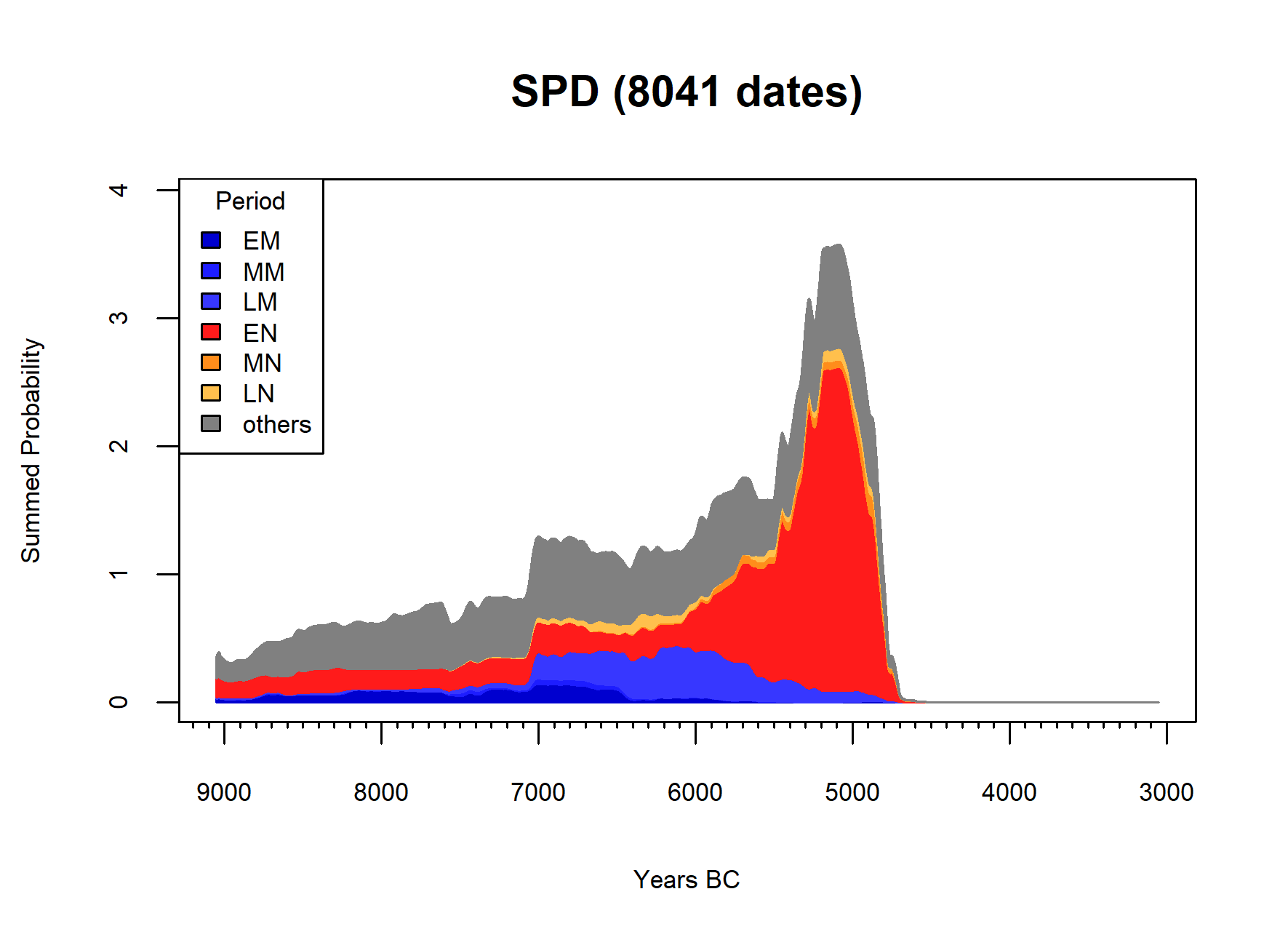
Baume de Montclus, stacked SPD
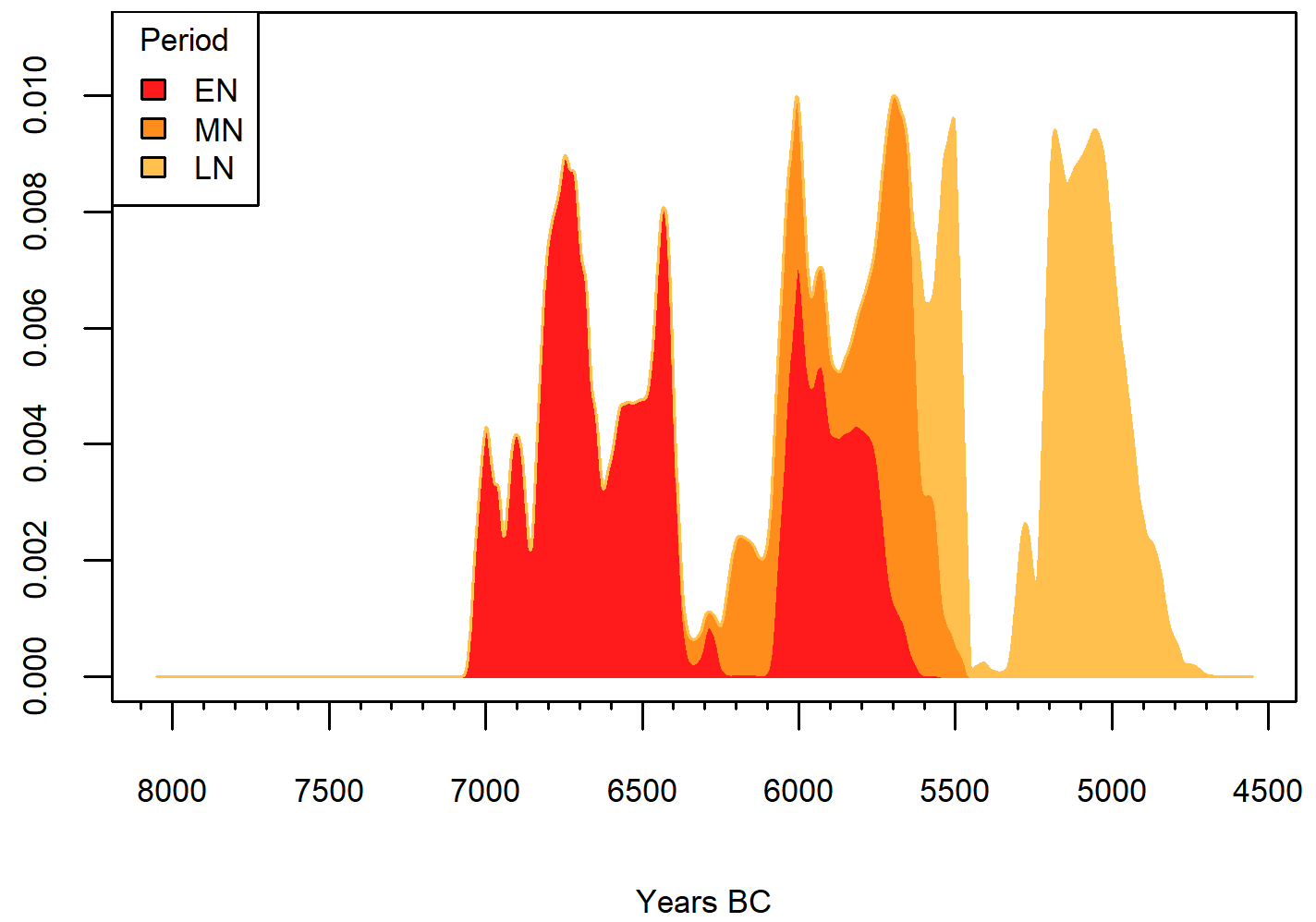
Franchthi cave, stacked SPD

- Open Data, Open Source, Open Access
- Scalable, Incrementable, Reusable, Analyzable
Materials and Methods
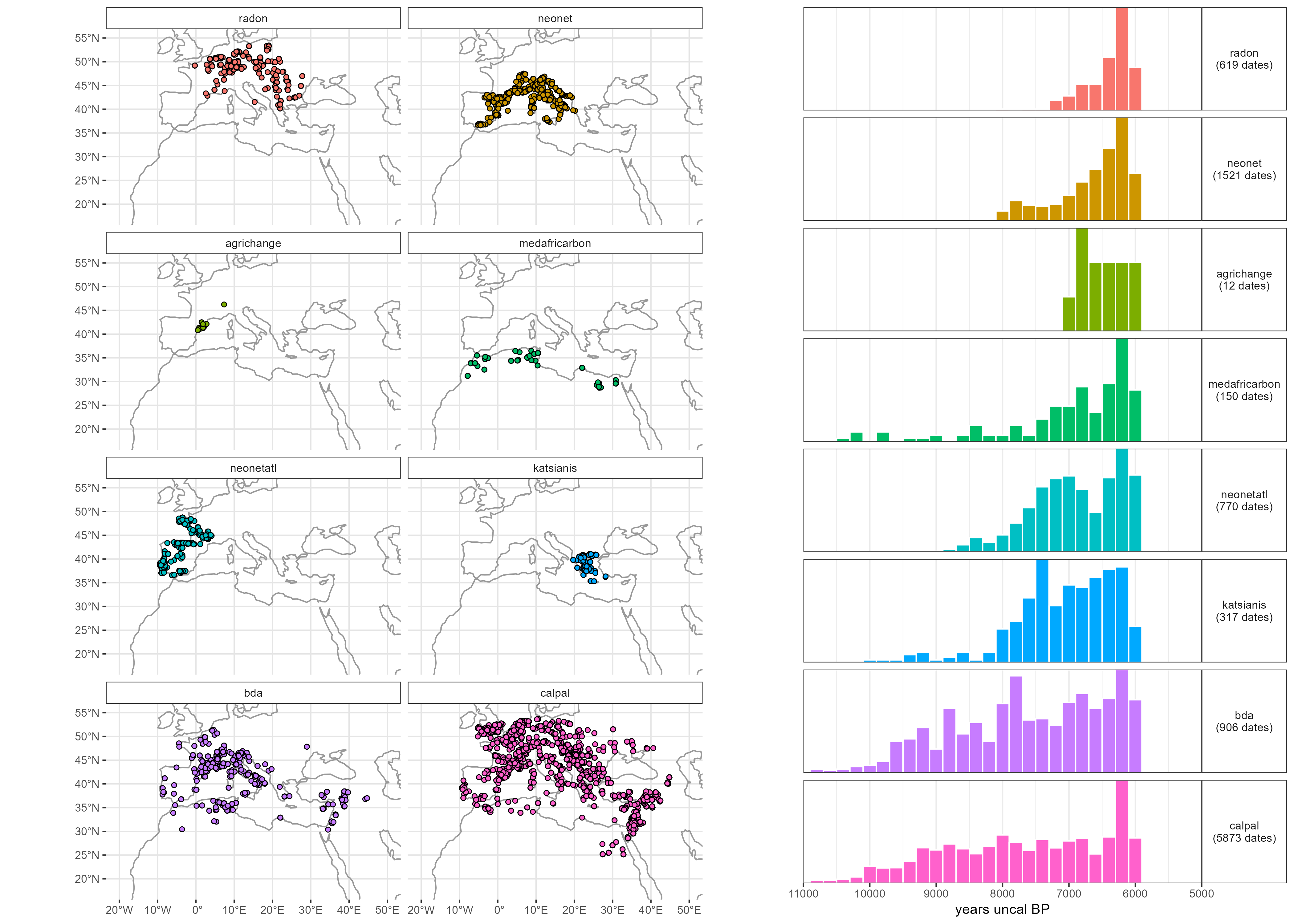
Radiocarbon dataset
| EM - Early Mesolithic |
| MM - Middle Mesolithic |
| LM - Late Mesolithic |
| EN - Early Neolithic |
| MN - Middle Neolithic |
| LN - Late Neolithic |
neonet-data-2023-10-22-select-aera.geojson
neonet-data-2023-10-22.geojson
Radiocarbon modelling
The most recent LM date median 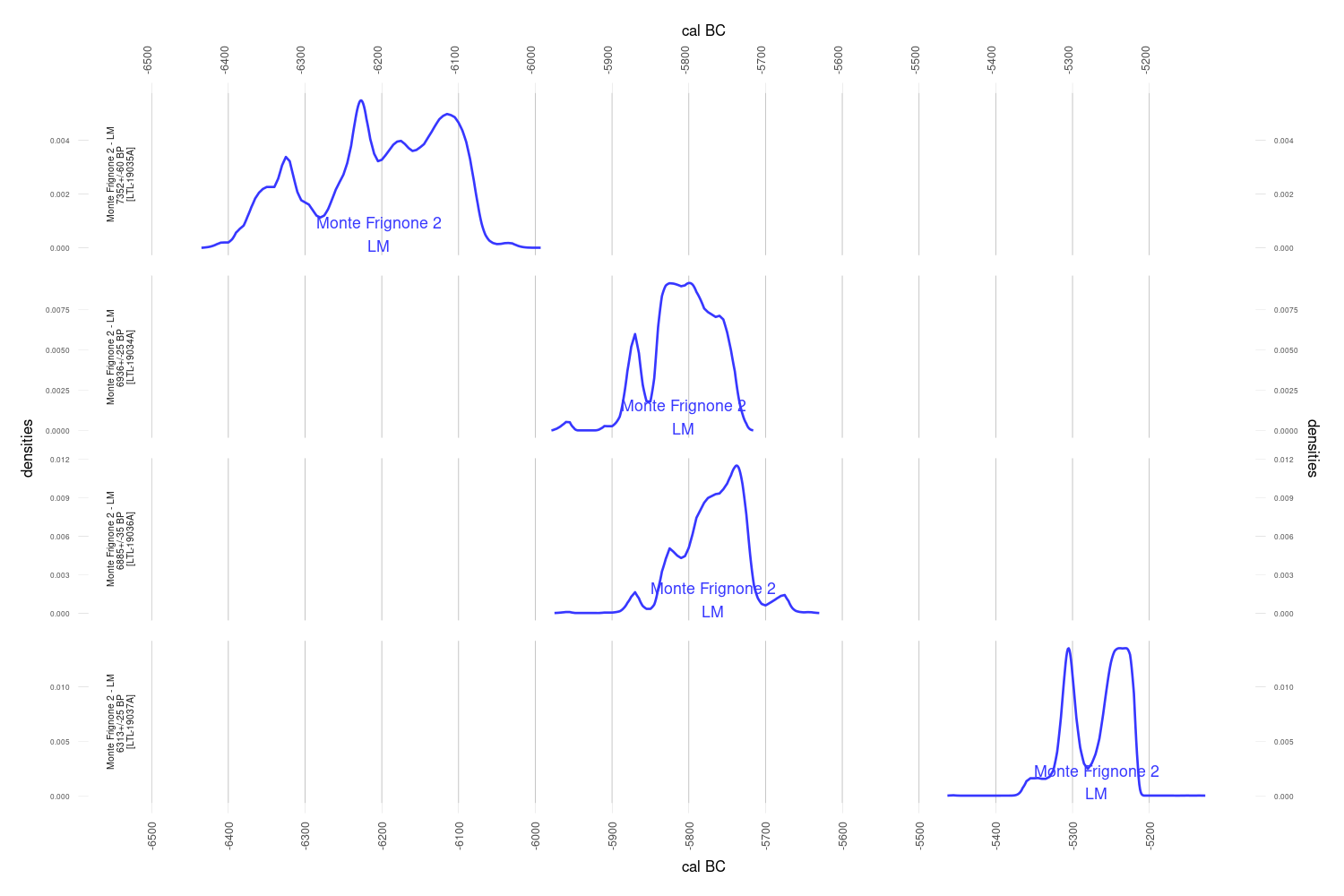
The most ancient EN date median 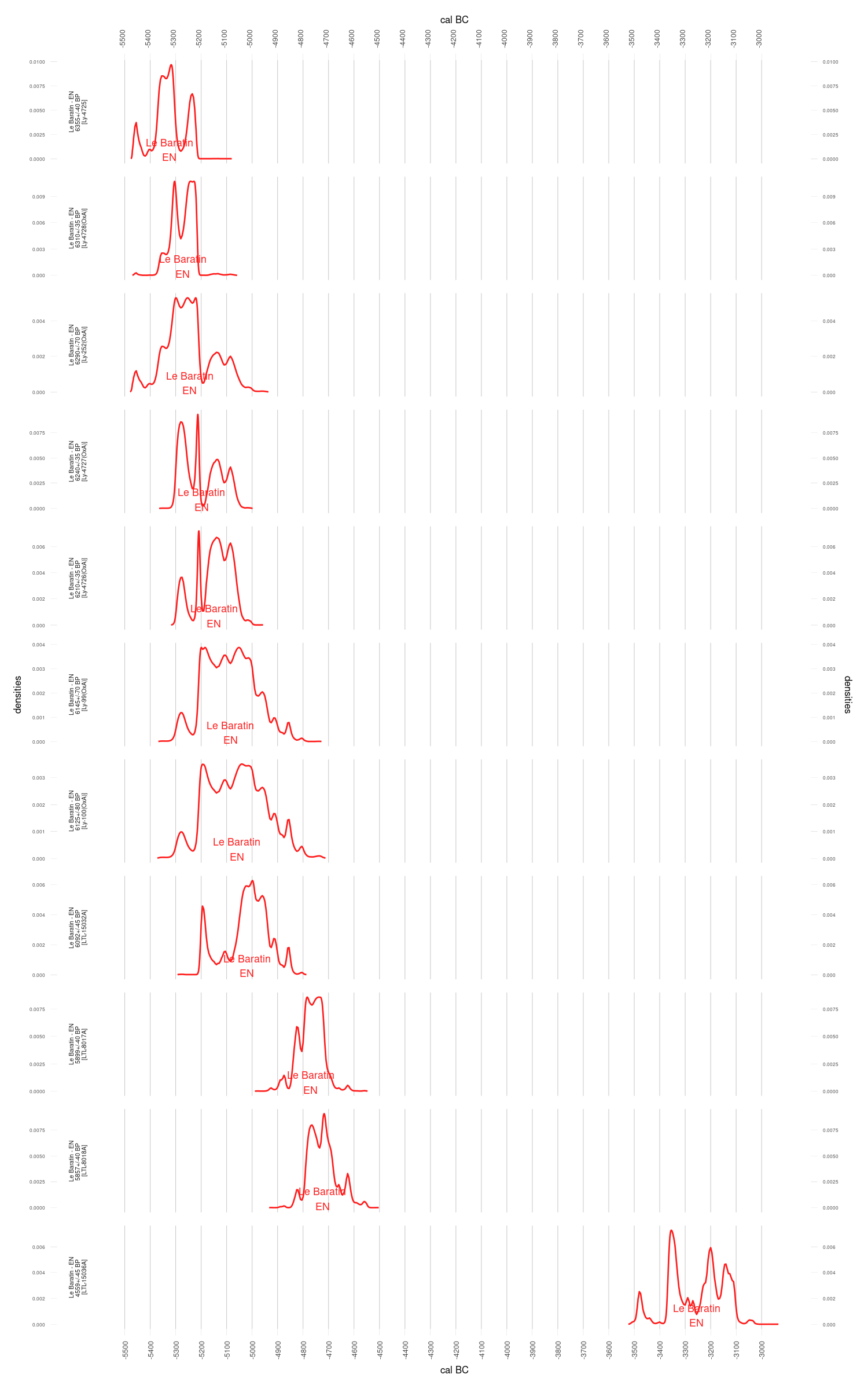

weighted.median <- matrixStats::weightedMedian(x = ages1$Date1$ageGrid,
w = ages1$Date1$densities)
df.c14[i, "median"] <- -(weighted.median - present)
if(stat.mean){
weighted.mean <- matrixStats::weightedMean(x = ages1$Date1$ageGrid,
w = ages1$Date1$densities)
df.c14[i, "mean"] <- -(weighted.mean - present)
}
df.c14[i, "tpq"] <- -(min(ages1$Date1$ageGrid) - present)
df.c14[i, "taq"] <- -(max(ages1$Date1$ageGrid) - present)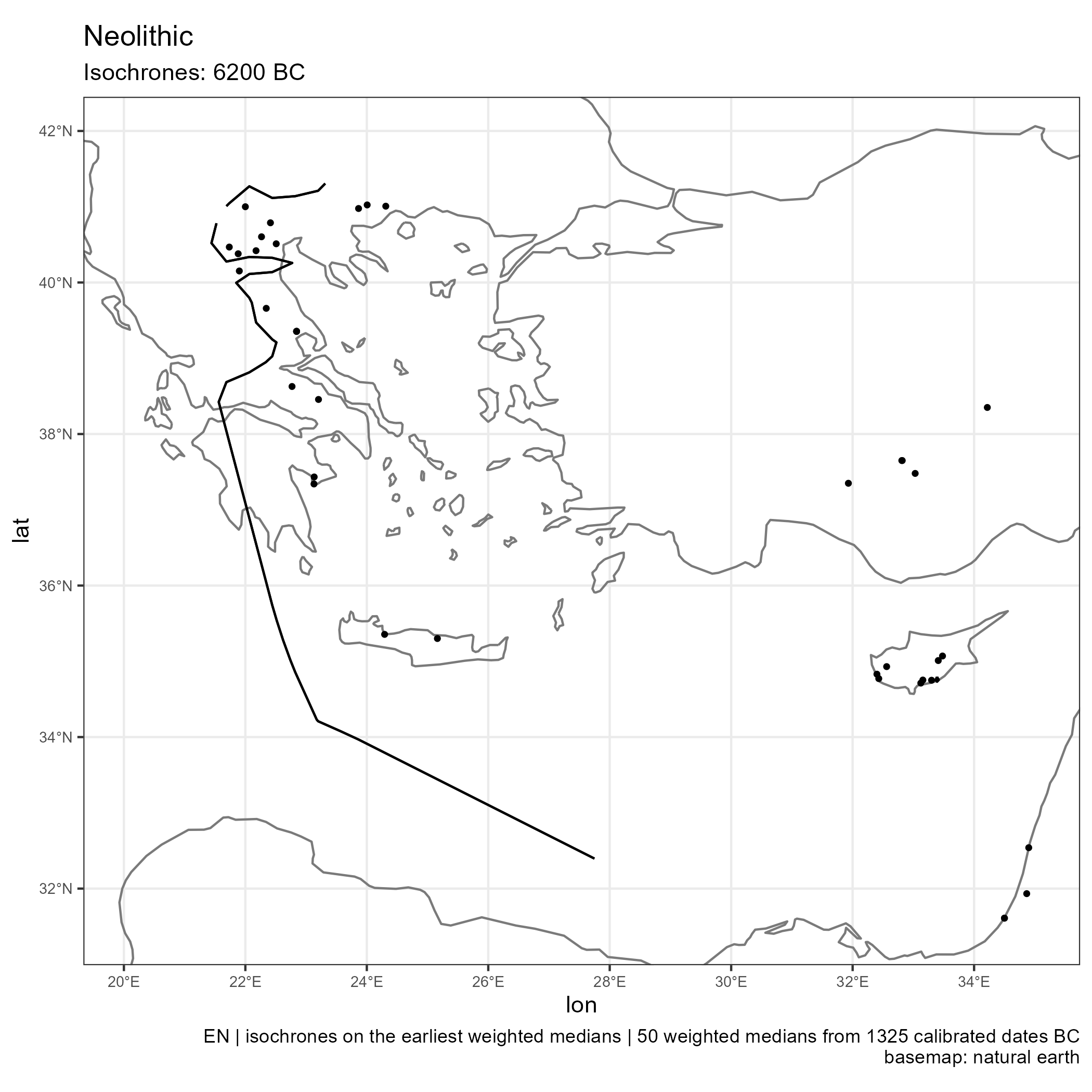
interpolated <- akima::interp(x = df$longitude,
y = df$latitude,
z = df$median,
duplicate = "mean")
interp_df <- tidyr::expand_grid(i = seq_along(interpolated$x),
j = seq_along(interpolated$y)) %>%
dplyr::mutate(lon = interpolated$x[i],
lat = interpolated$y[j],
date.med = purrr::map2_dbl(i, j, ~interpolated$z[.x, .y])) %>%
dplyr::select(-i, -j)Climates data
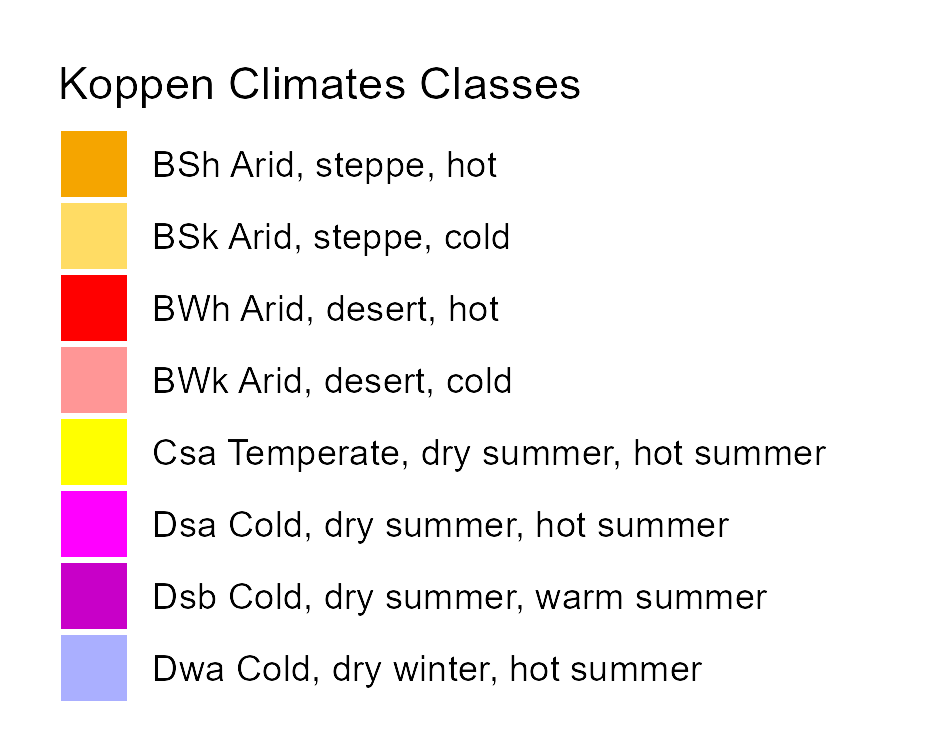
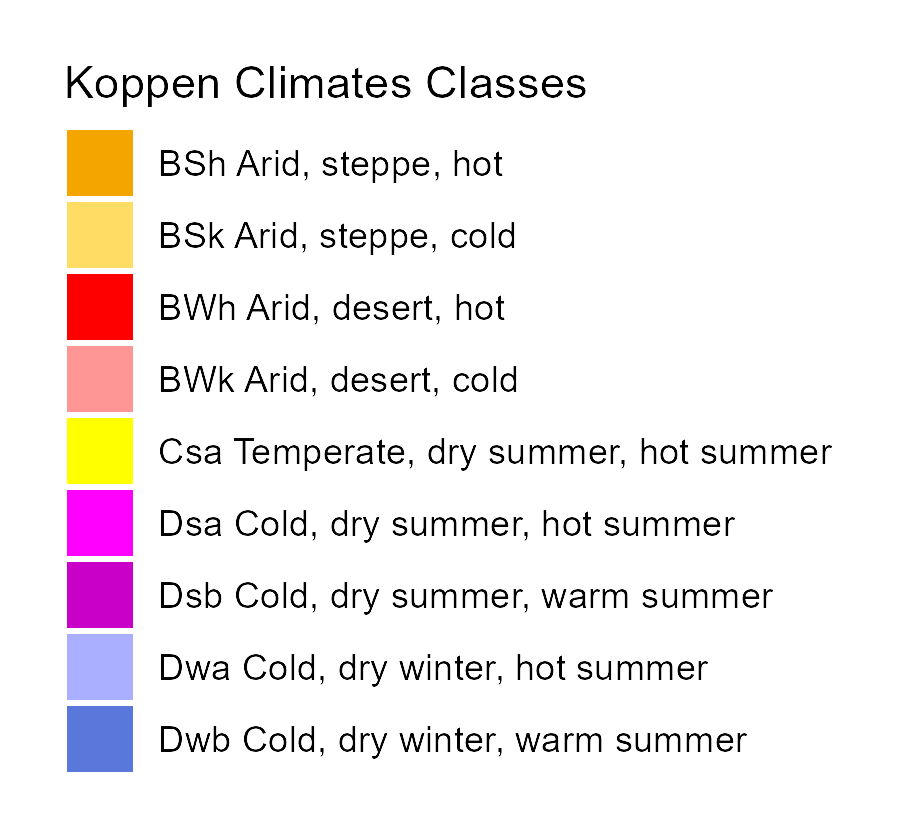
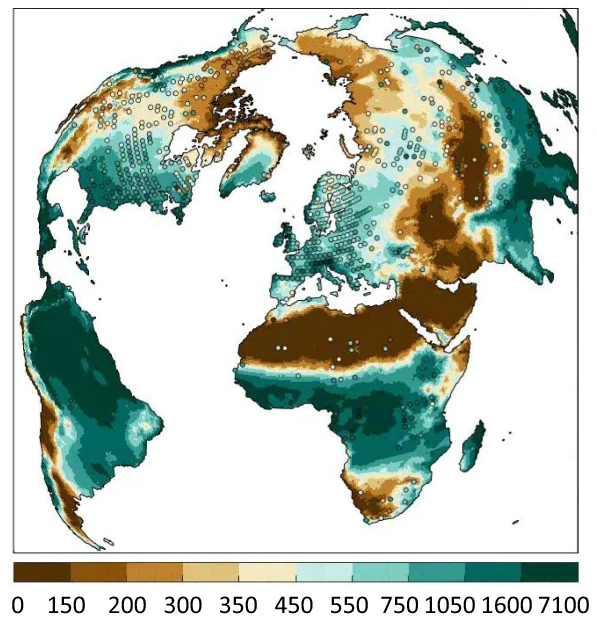
Mean annual temperature (ºC)
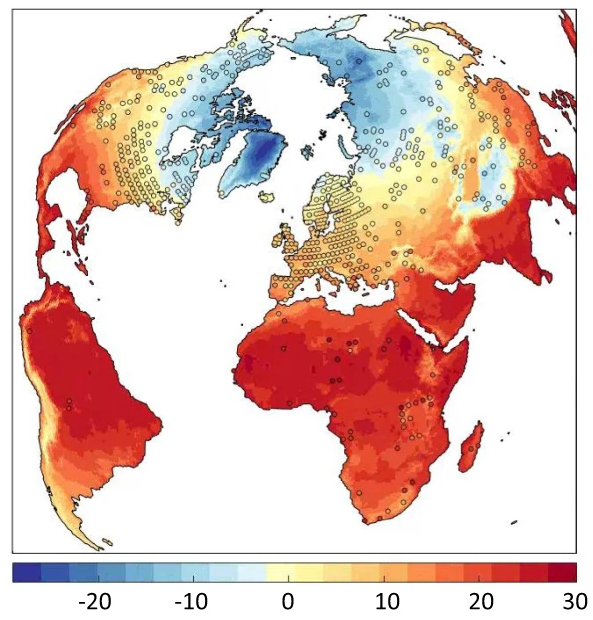
Annual precipitation (mm year -1)
Biome (pollen-based)
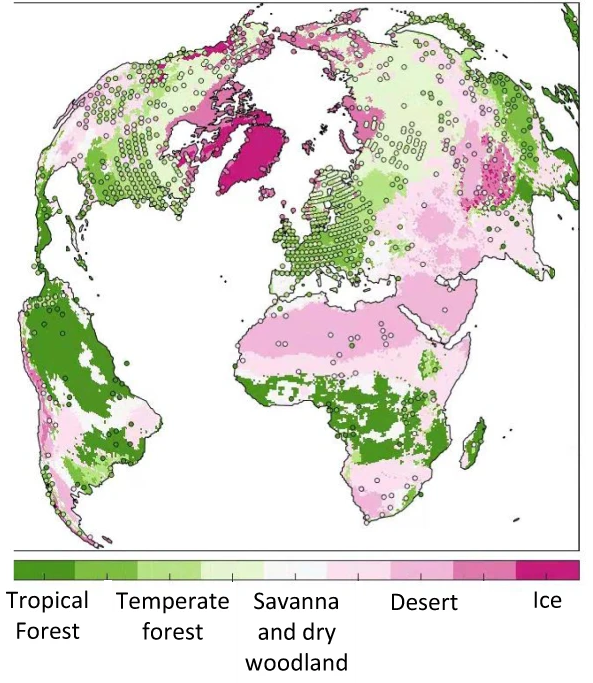
Beyer et al. 20201
Climate dating by site
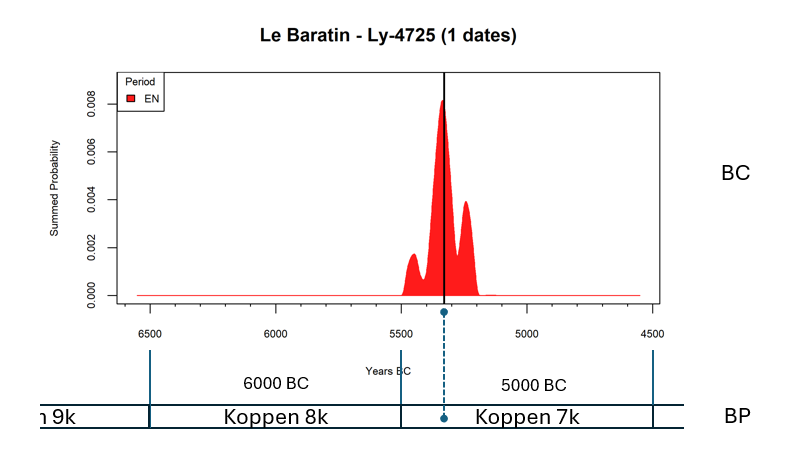
52: Le Baratin, Ly-4725
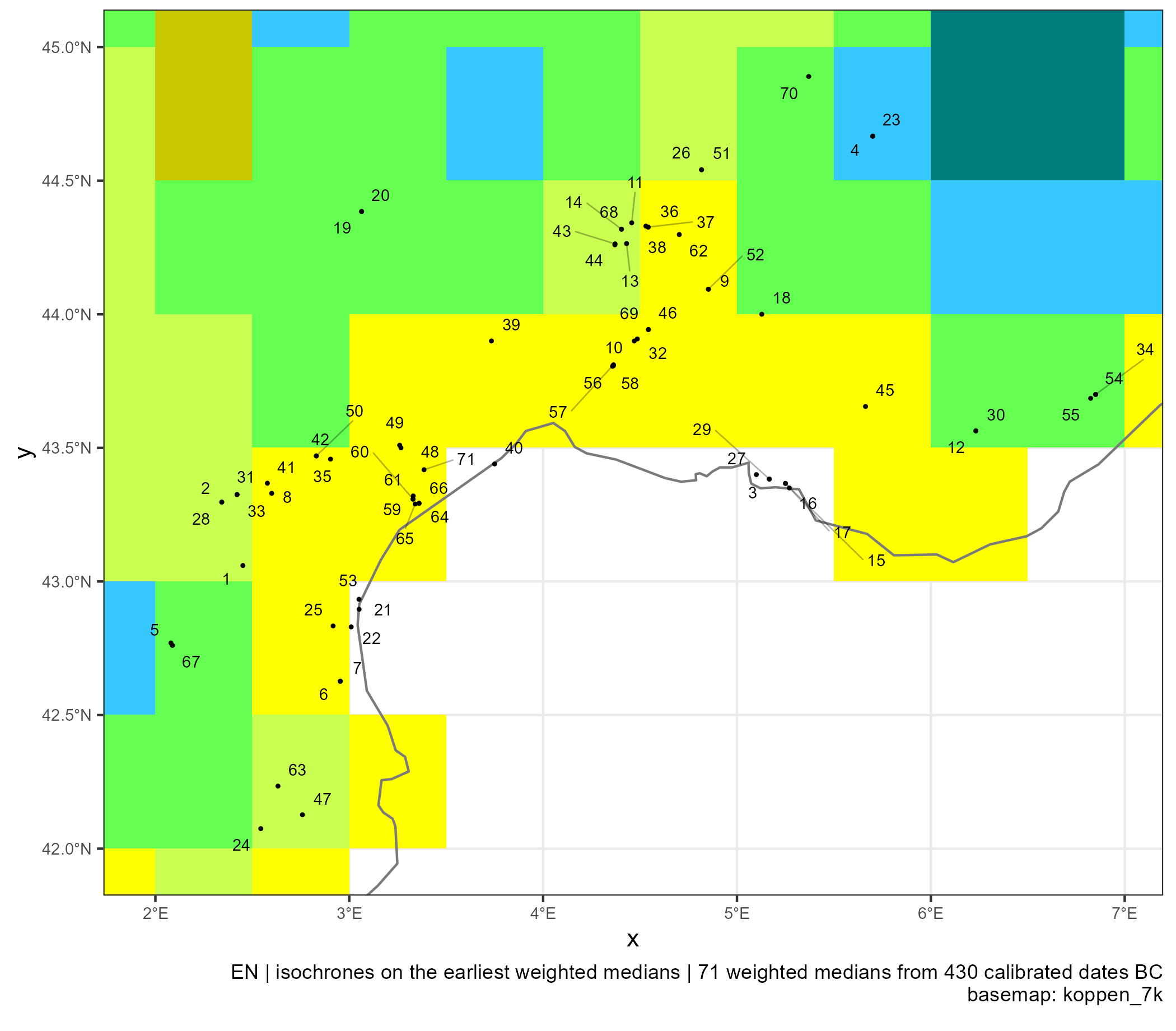


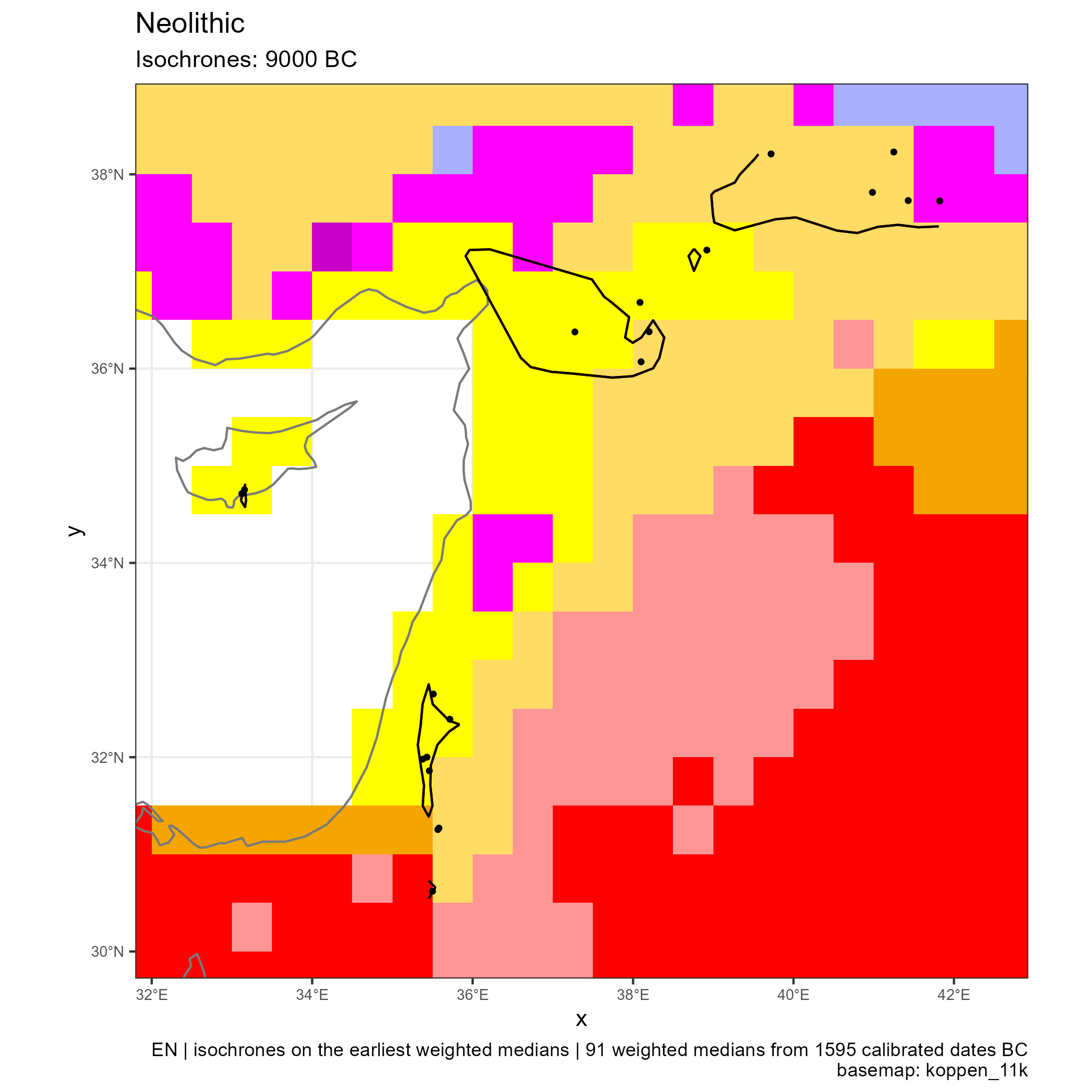
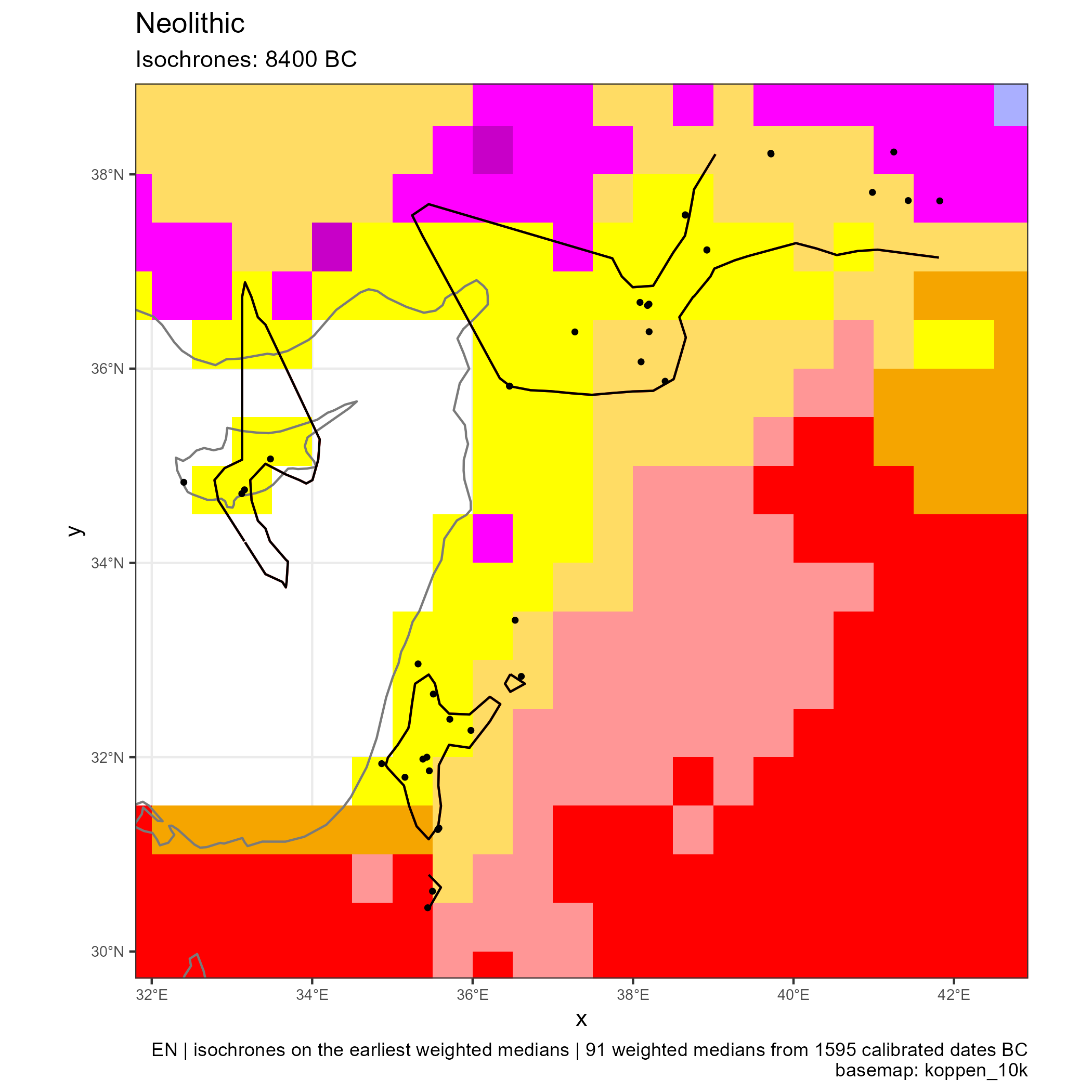
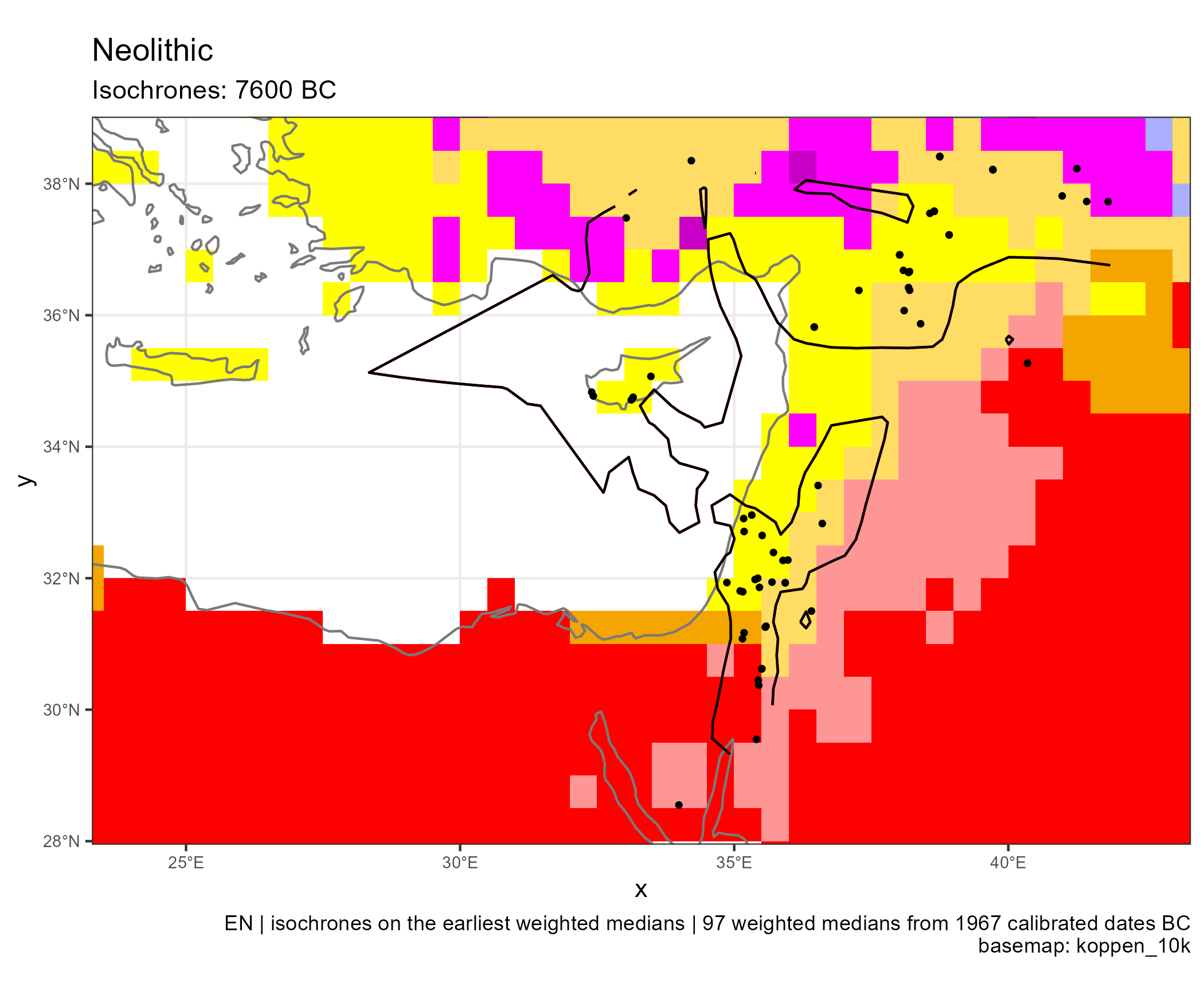
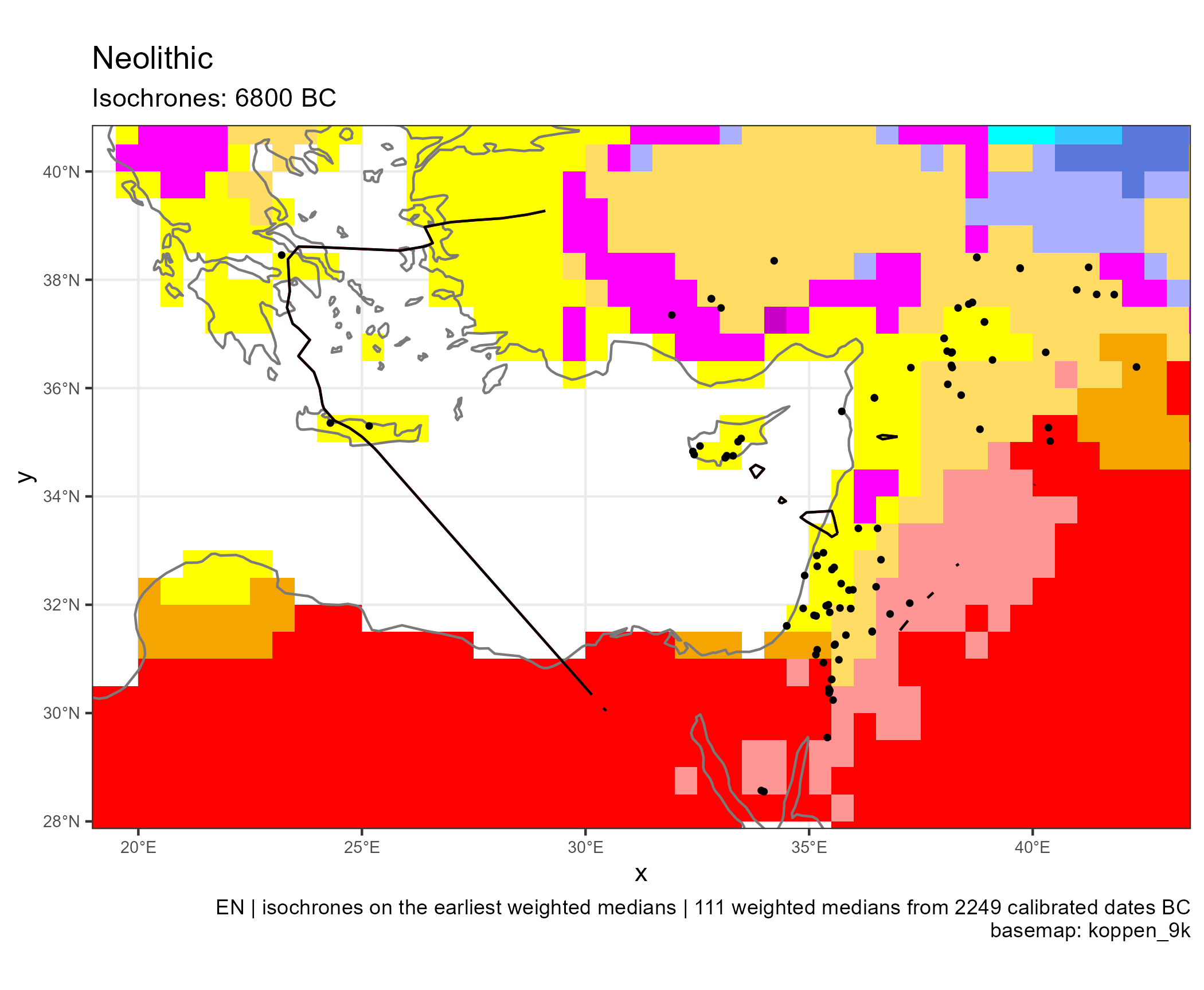
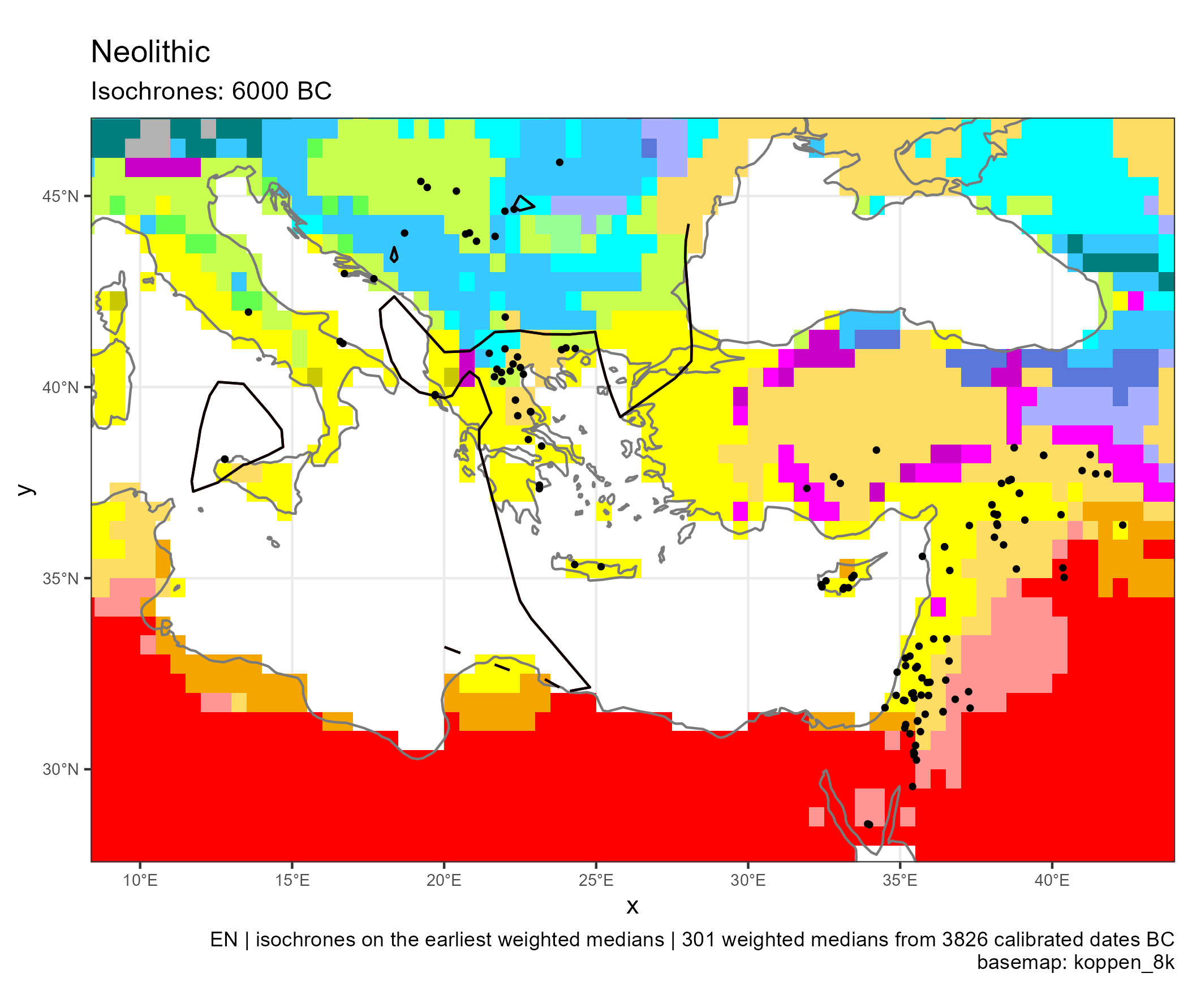
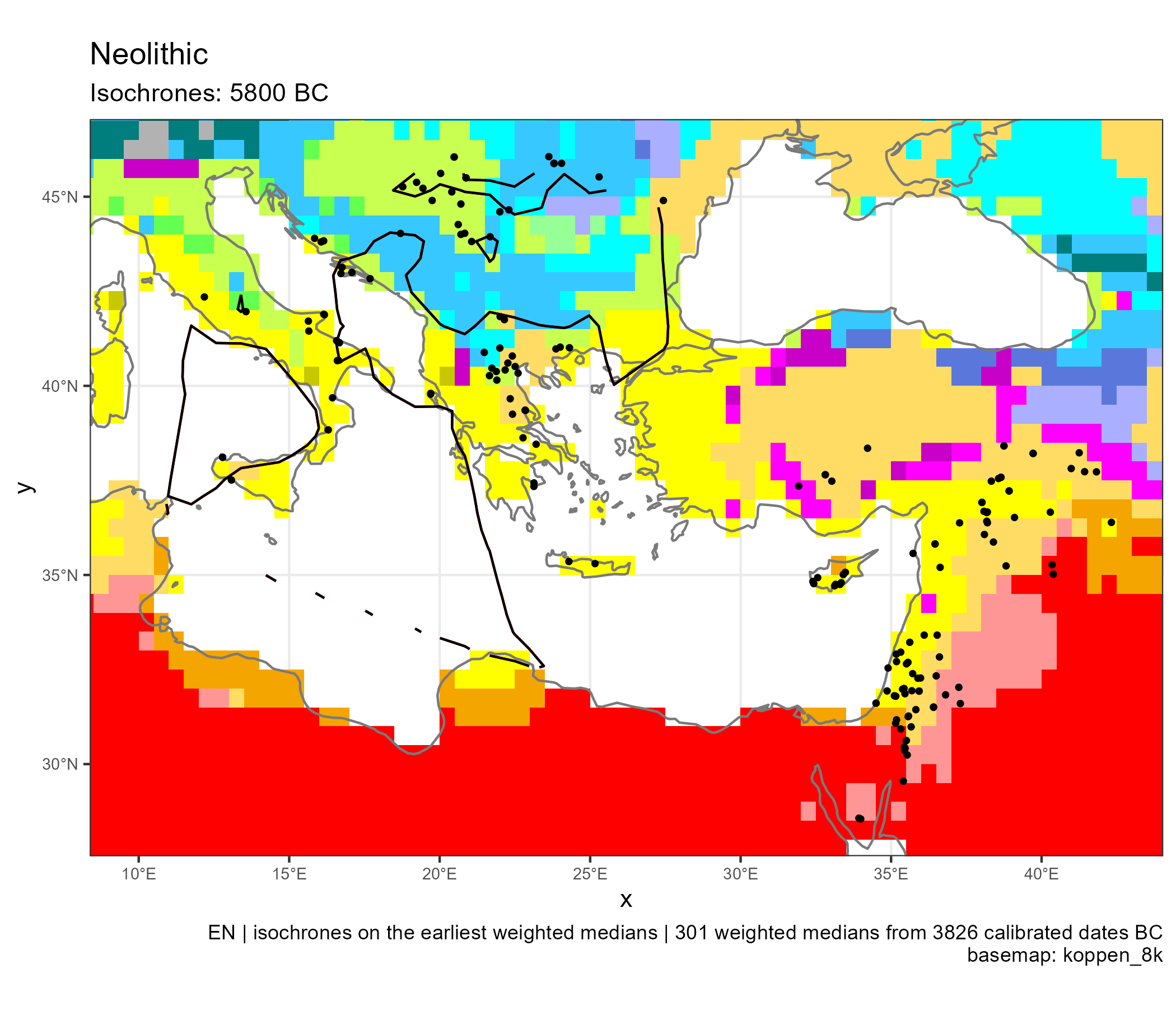
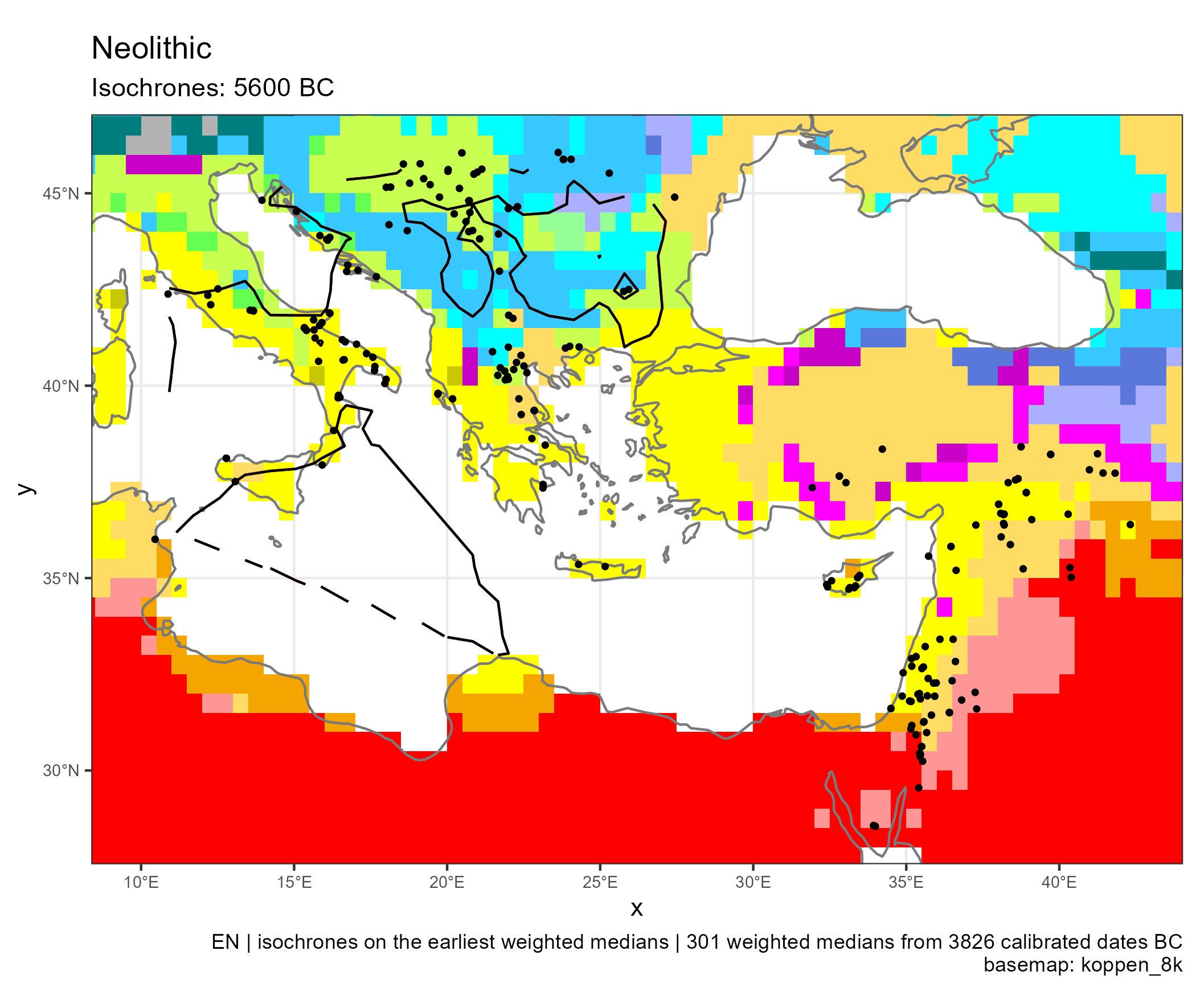
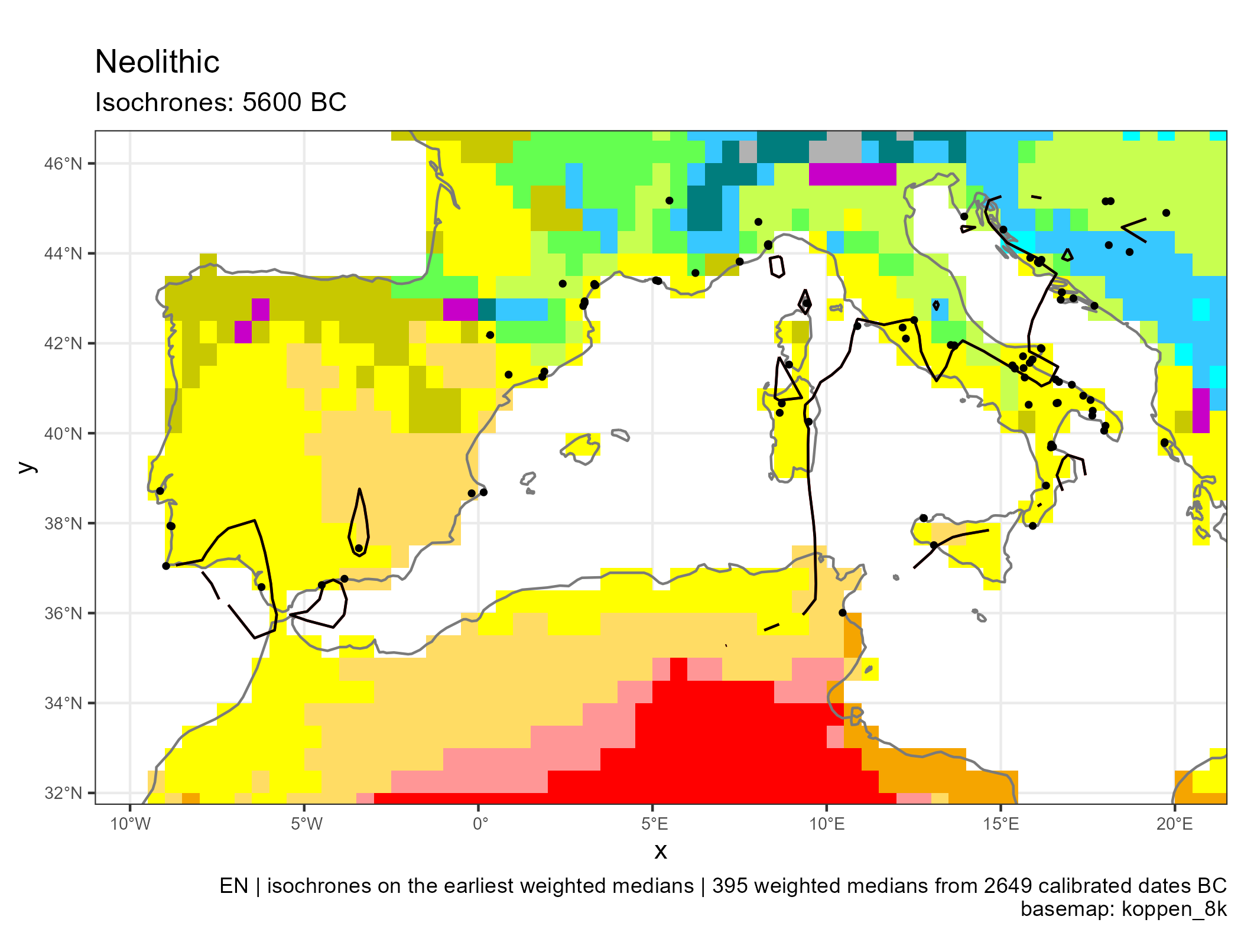
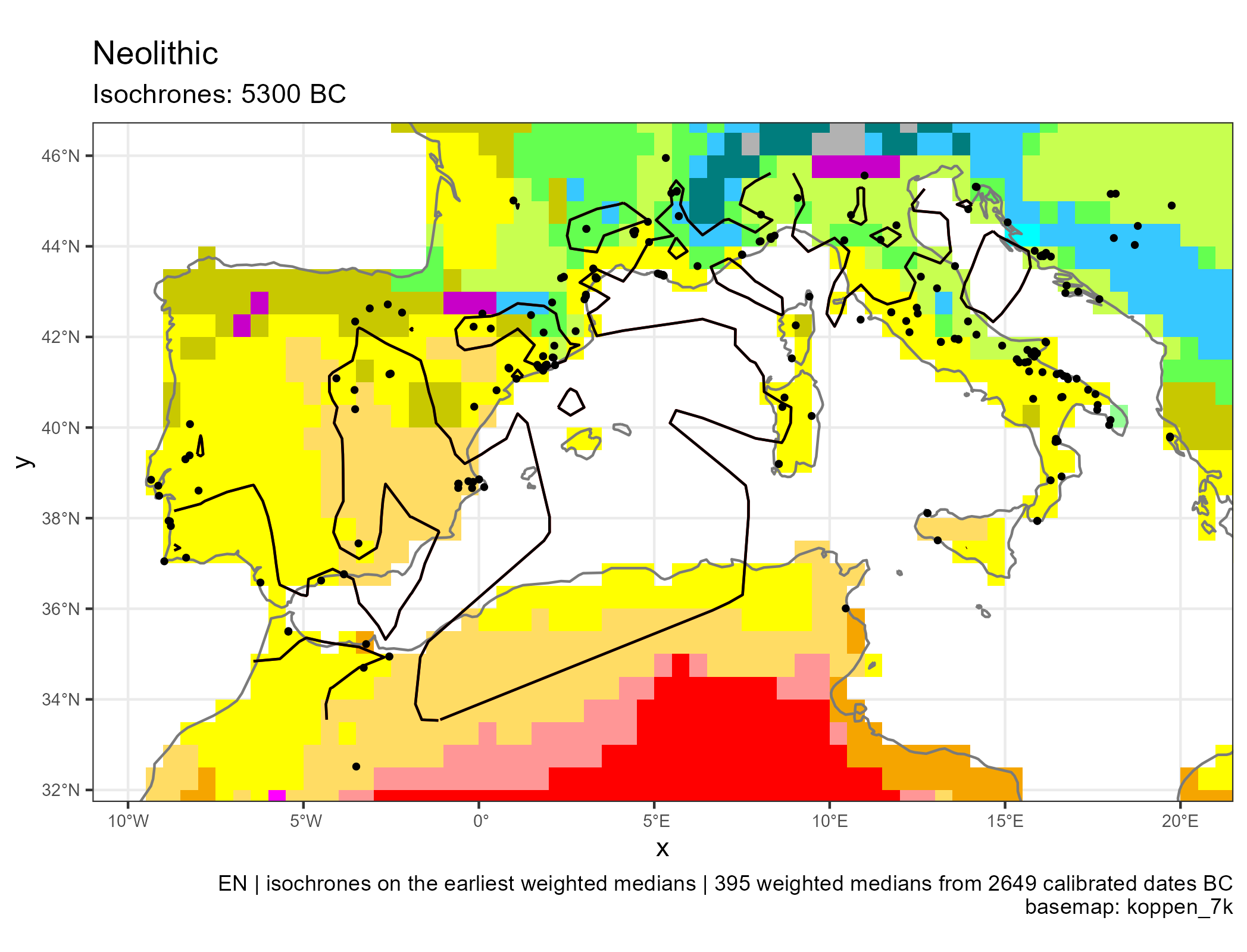
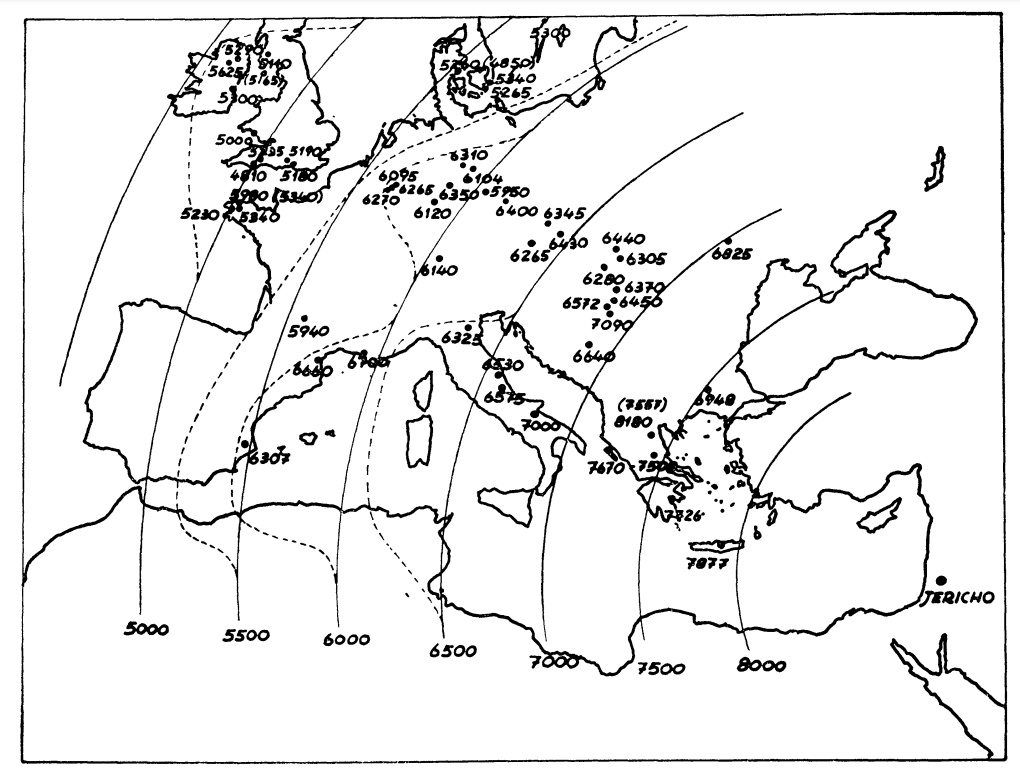
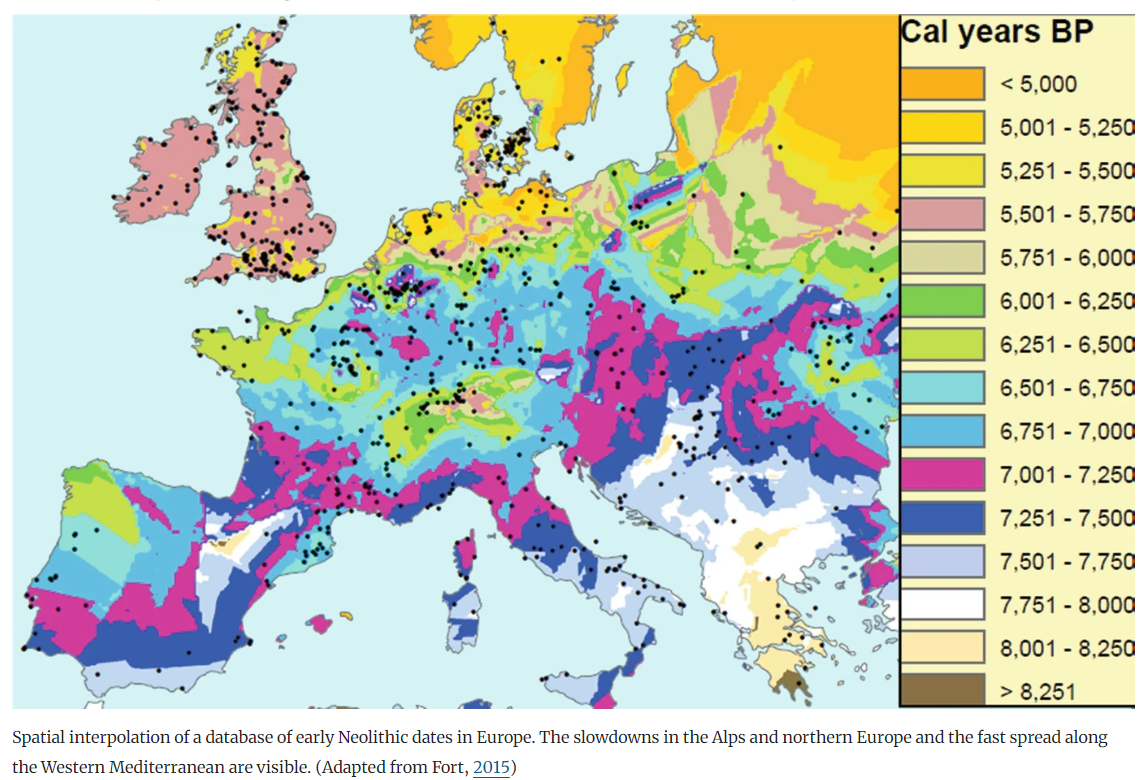
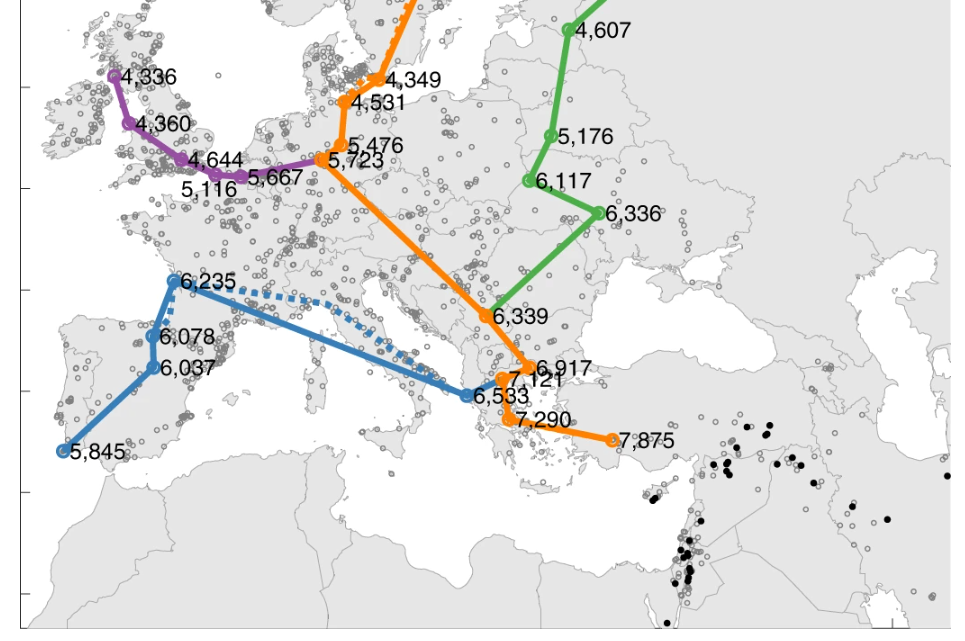
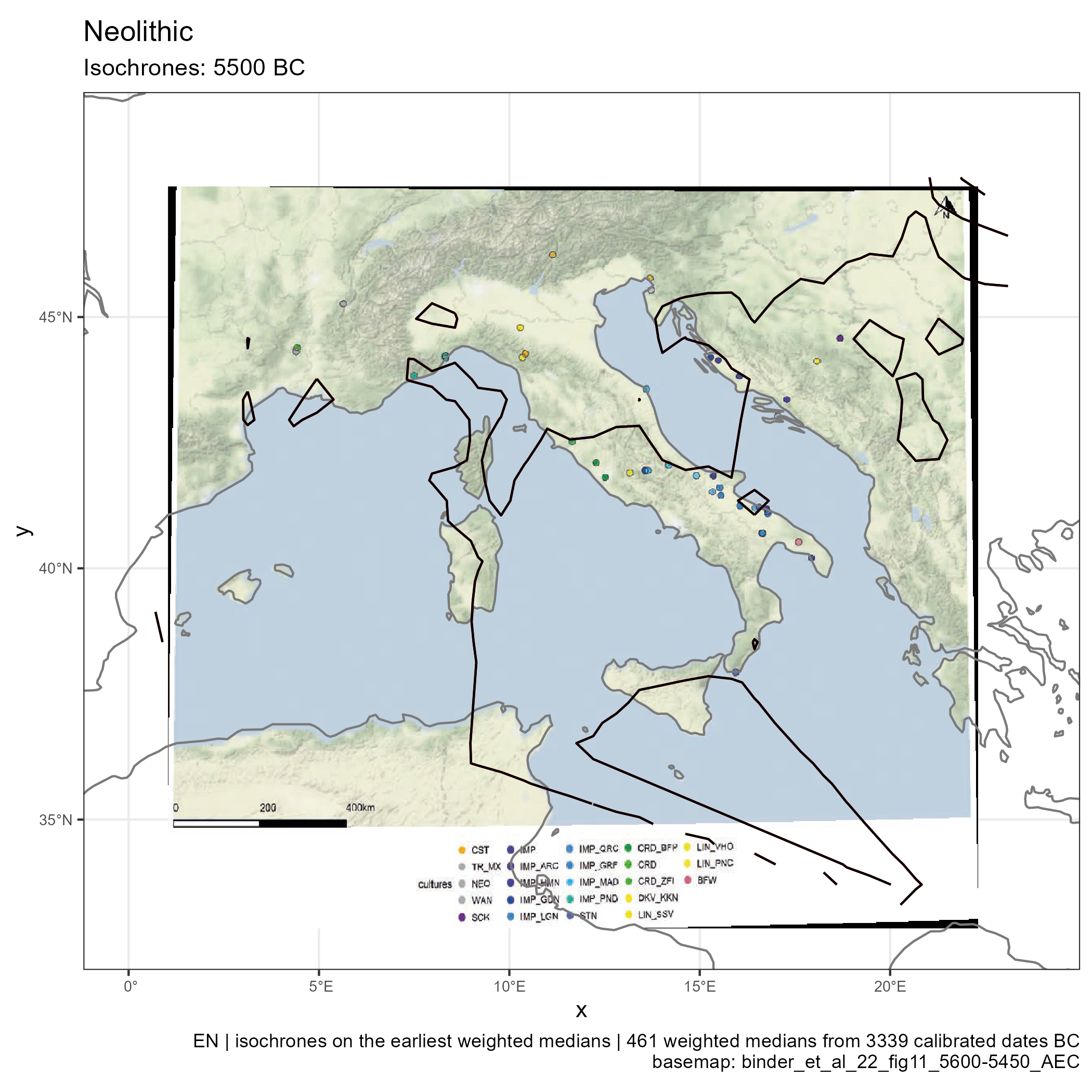
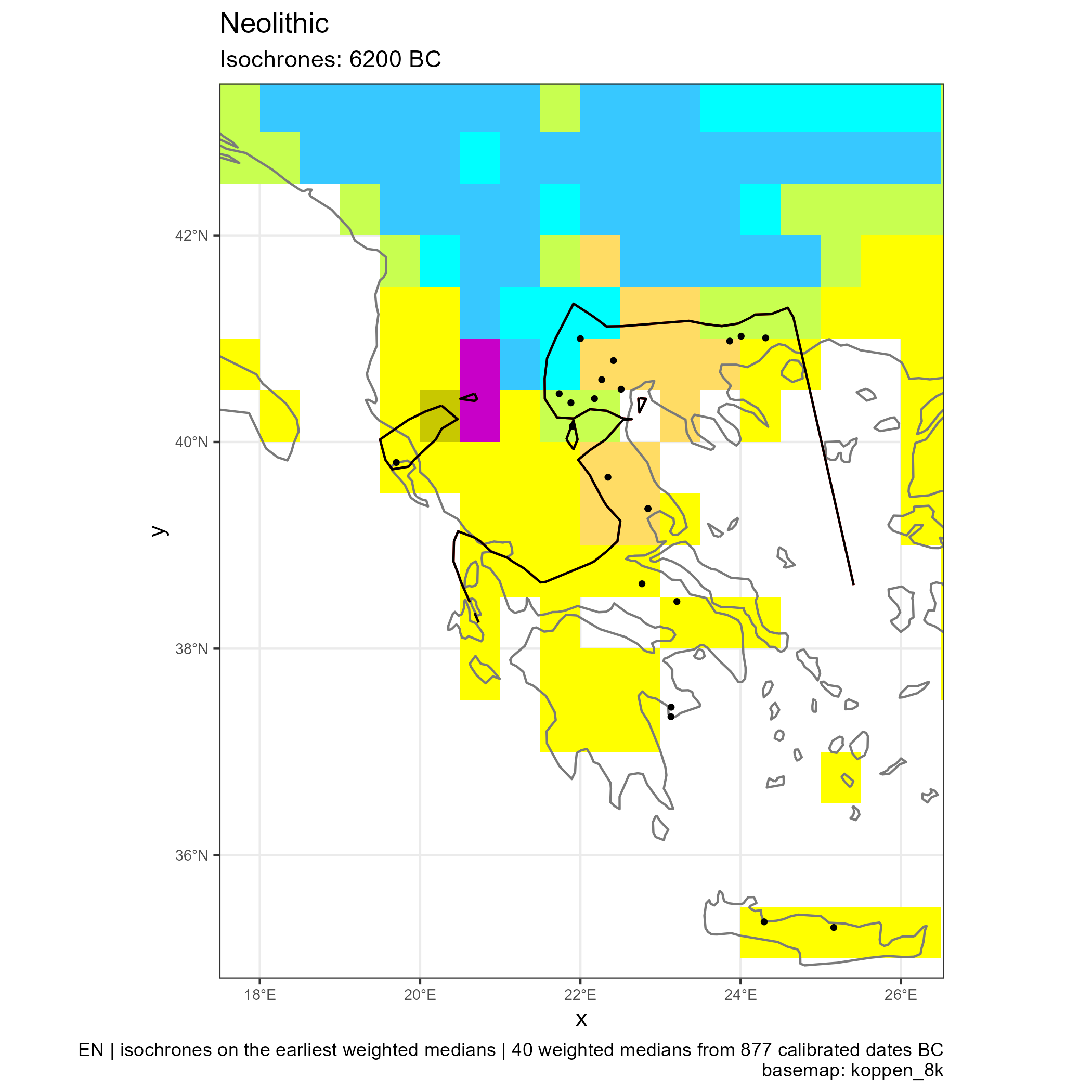
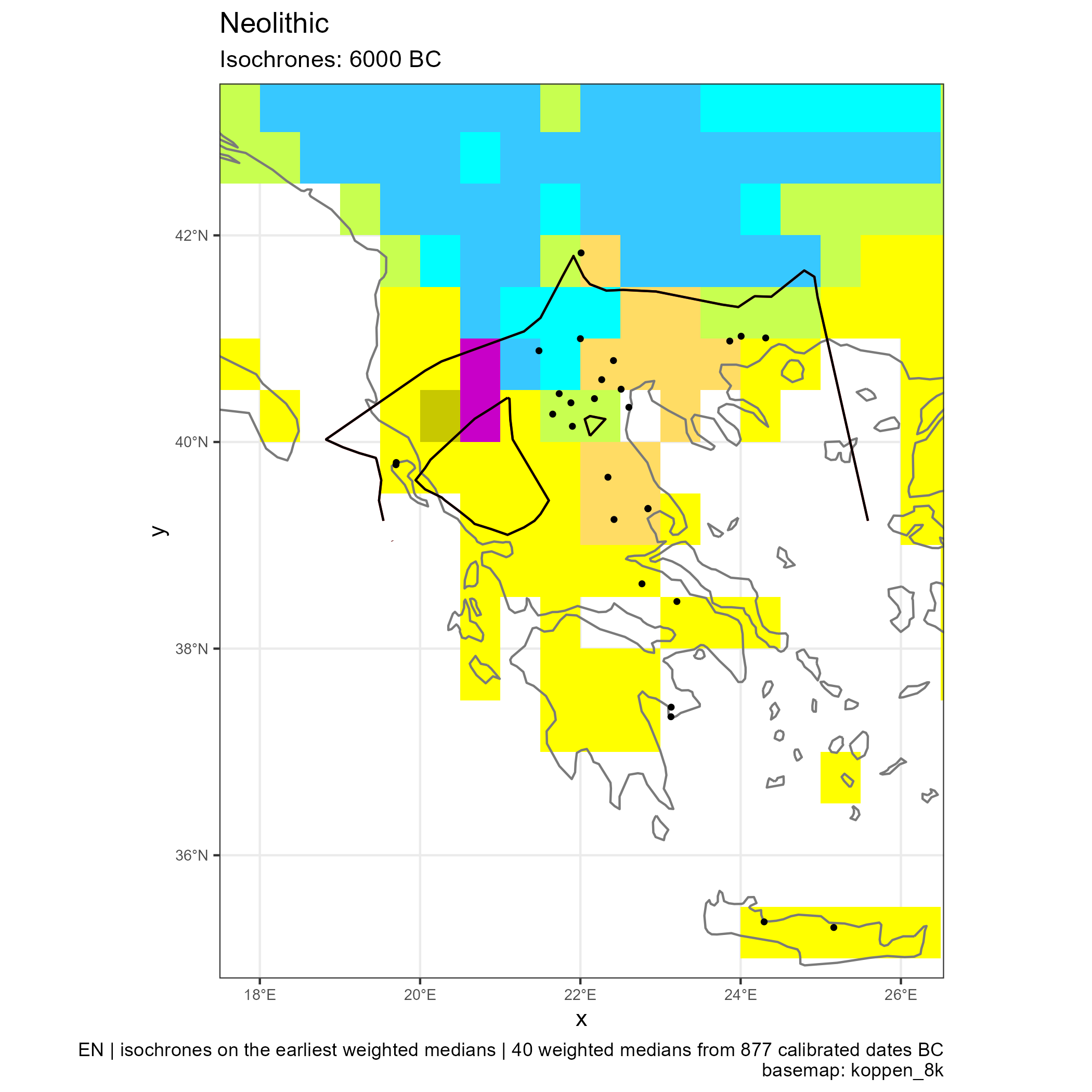
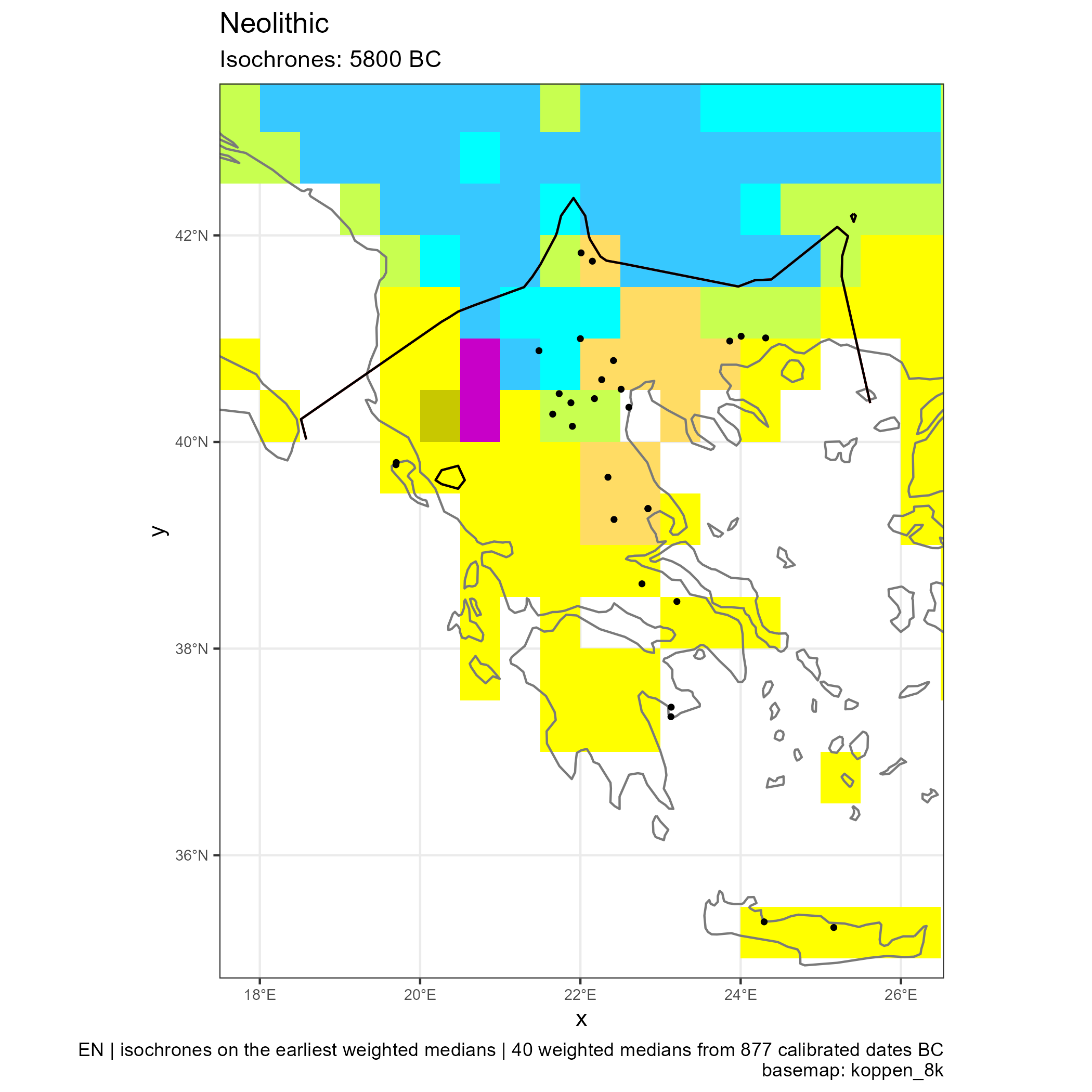
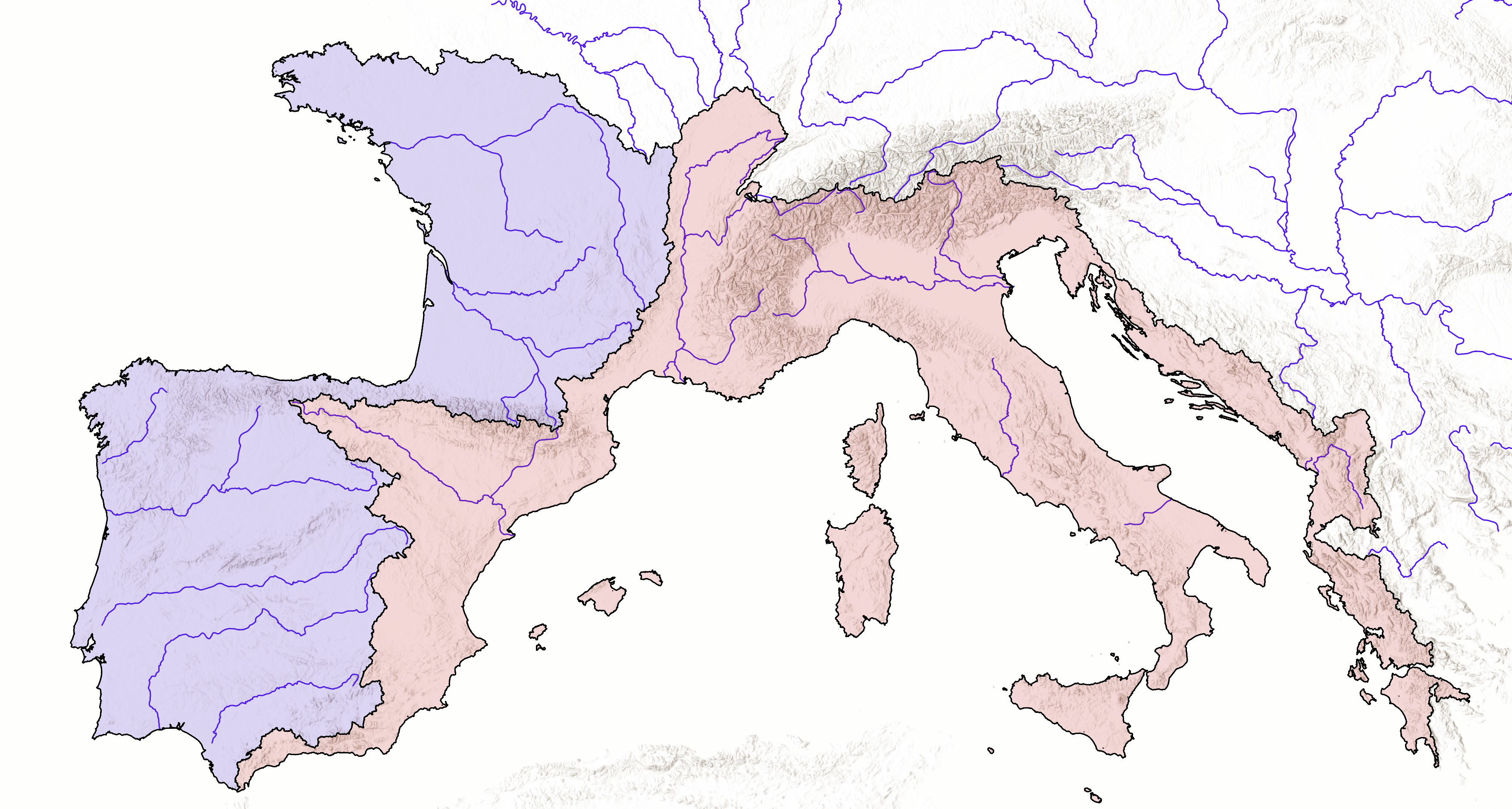
Spread of Neolithic the Mediterranean
Eastern and Central Mediterranean (in BC)
Western Mediterranean (in BC)
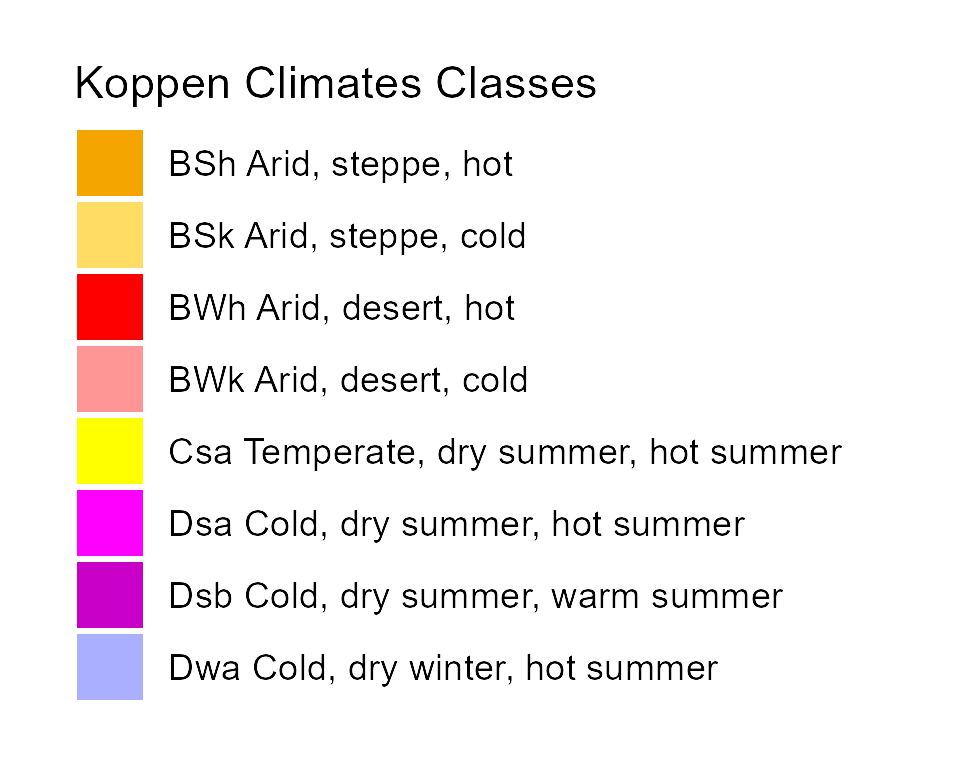
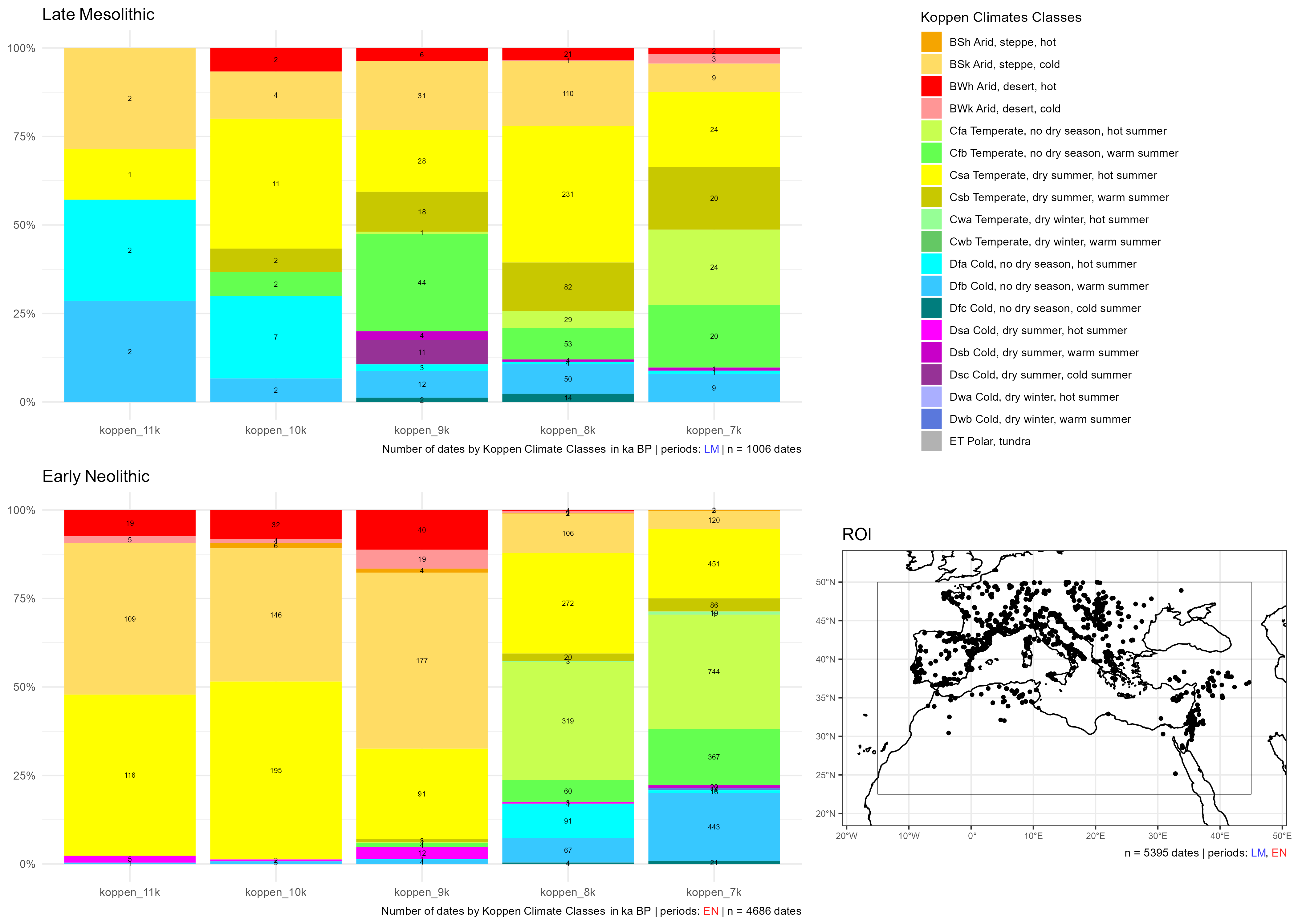
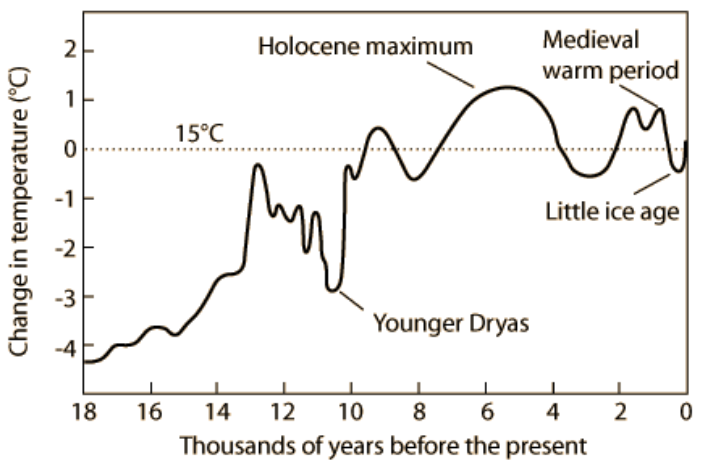
Climates evolution
Discussion
 productible methods
productible methods
Thank you
Footnotes
Beyer, R. M., Krapp, M., & Manica, A. (2020). High-resolution terrestrial climate, bioclimate and vegetation for the last 120,000 years. Scientific data, 7(1), 236.
Ammerman, A. J., & Cavalli-Sforza, L. L. (1971)[^2]. Measuring the rate of spread of early farming in Europe. Man, 674-688.
Fort, J. (2022). The spread of agriculture: quantitative laws in prehistory?. In Simulating Transitions to Agriculture in Prehistory (pp. 17-28). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
Betti, L., Beyer, R. M., Jones, E. R., Eriksson, A., Tassi, F., Siska, V., … & Manica, A. (2020). Climate shaped how Neolithic farmers and European hunter-gatherers interacted after a major slowdown from 6,100 BCE to 4,500 BCE. Nature Human Behaviour, 4(10), 1004-1010.
Binder, D., Angeli, L., Gomart, L., Huet, T., Maggi, R., Manen, C., … & Tagliacozzo, A. (2019, March). L’Impresso-cardial du nord-ouest et ses rapports avec la «zone-source»: une synthèse chrono-culturelle. In Céramiques imprimées de Méditerranée occidentale. Matières premières, productions, usages.